CHAPTER 3
SHIP COMPARTMENTATION AND WATERTIGHT
INTEGRITY
watertight integrity, and how they relate to each other.
Learning Objectives: Recall the definitions of terms
You will also learn about compartment checkoff lists,
used to define the structure of the hull of a ship and the
the DC closure log, the proper care of access closures
numbering systems used for compartment number
and fittings, compartment inspections, the ship's draft,
designations. Identify the different types of watertight
and the sounding and security patrol watch. The
closures and recall the inspection procedures for the
information in this chapter will assist you in
closures. Recall the requirements for the three material
completing your personnel qualification standards
conditions of readiness, the purpose and use of the
(PQS) for basic damage control.
Compartment Checkoff List (CCOL) and damage
control closure log, and the procedures for checking
COMPARTMENTATION
watertight integrity.
A ship's ability to resist sinking after sustaining
Learning Objective: Recall the definitions of terms
d a m a g e d e p e n d s l a r g e l y o n t h e s h i p 's
used to define the structure of the hull of a ship and the
compartmentation and watertight integrity. When
numbering systems used to identify the different
these features are maintained properly, fires and
compartments of a ship.
flooding can be isolated within a limited area. Without
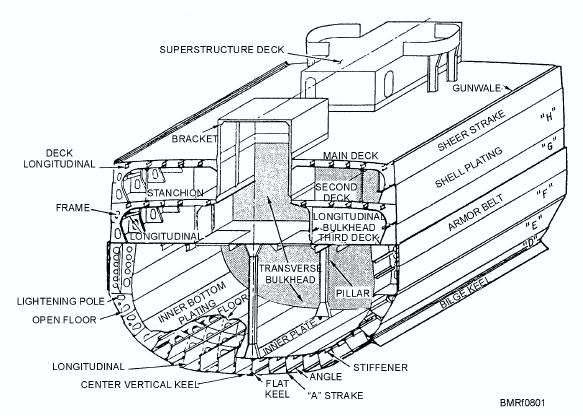
The compartmentation of a ship is a major feature
compartmentation or watertight integrity, a ship faces
of its watertight integrity. Compartmentation divides
almost certain doom if it is severely damaged and the
the interior area of a ship's hull into smaller spaces by
emergency damage control (DC) teams are not
the use of structural members.
properly trained or equipped.
Refer to figure 3-1 while reviewing the information
I n t h i s c h a p t e r, y o u w i l l b e i n t r o d u c e d t o
on structural members.
compartmentation, material conditions of readiness,
Figure 3-1. Illustrative hull structure.
3-1

