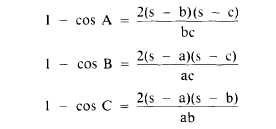The value s means one-half the sum of sides
a, b, and c, or
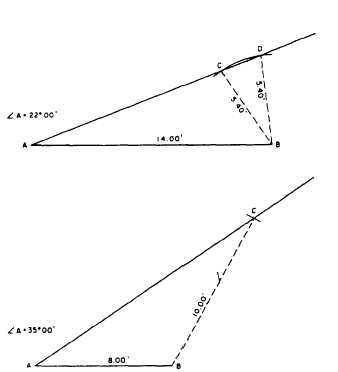
Figure 1-29.-Comparison of an ambiguous case triangle to
a standard triangle.
might satisfy this situation. Both triangles shown
are with given angle A = 30°00´, given side
a = 4.00 ft, and given side c = 6.00 ft.
The best way to determine whether or not the
given data for a triangle involves an ambiguous
case is to lay out a figure to scale on the basis of
the data, as shown in figure 1-29. Suppose, for
example, that the data describes a triangle with
angle A = 22°00'; side opposite, 5.40 ft; and
other side, 14.00 ft. Lay off a line, AB, 14.00 ft
long (to scale, of course), as shown in the upper
triangle of figure 1-29. Use a protractor to lay off
a line from A at 22°00'. Set a compass to the
graphical distance of 5.40 ft (length of side
opposite A) and with B as a center, strike an arc.
You observe that this arc intersects the line from
A at two places. Therefore, the triangle ACB and
the triangle ADB both satisfy the data, and you
have an ambiguous case.
Suppose now that the data describes a triangle
with angle A = 35°00´; side opposite, 10.00 ft;
and other side, 8.00 ft. Lay off the line AB 8.00
ft long as shown in the lower triangle of figure
1-29, and lay off a line from A at 35°00’, Set a
compass to 10.00 ft (length of side opposite A)
and with B as a center, strike an arc. This arc will
intersect the line from A at only one point.
Therefore, only one triangle satisfies the data.
Determination of Angle
from Three Known Sides
There are several formulas for determining the
size of an angle in a triangle from three known
sides. The most convenient involves the versed sine
of the angle, which means (1 -cos) of the angle.
The formula goes as follows:
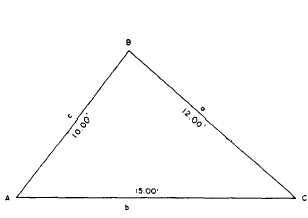
For the triangle shown in figure 1-30, you would
determine the size of angle A as follows:
The angle with cosine 0.60333 measures (to the
nearest minute) 52°53´.
Figure 1-30.—Oblique triangle with three sides given and
solved by versed sine formula.
1-24