Figure 4-8.-Dividing a line into proportional parts.
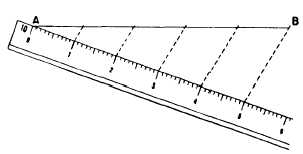
Figure 4-7.-Using a scale to lay off equal intervals on a
random line.
to A, and project the other points of intersection
from CB to AB by lines parallel to the first one.
The projected points of intersection divide AB
into 10 equal parts.
Figure 4-7 shows how you can use a scale to
lay off equal intervals on the ray line.
DIVISION INTO
PROPORTIONAL PARTS
Figure 4-8 show’s a method of dividing
a line into given proportional parts. The
problem here is to divide the line AB into
parts that are proportional as 2:3:4. Lay
off ray line CB from B at a convenient
acute angle to AB. Set a compass to a
convenient spread, and lay off this interval
from B on CB the number of times that
is equal to the sum of the figures in the
proportion (2 + 3 + 4 = 9). Draw a line from
the point of intersection of the last interval
to A, and use a straightedge and triangle to
project the second and fifth intercepts on CB
to AB by lines parallel to the first one. The
projected intercepts divide AB into segments
that are proportional as 2:3:4.
Here again, you could use a scale to lay off
nine equal intervals on CB.
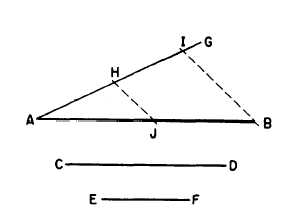
Figure 4-9.-Dividing a line into parts according to a given
ratio.
of doing this is shown in figure 4-9. Here,
it is required that AB be divided so that
the ratio between AB and a part of AB
is the same as the ratio between CD and
EF. From A, draw a ray line AG at a convenient
acute angle from AB. On AG, lay off AH
equal to EF and AI equal to CD. Draw
a line from I to B, and use a straightedge
and triangle to project H to J on a line
parallel to IB. The ratio of AB to AJ is the same
as that of CD to EF.
ANGLES
You already know how to lay off an
angle of given size with a protractor, or
trigonometrically by the use of the tangent or the
chord method.
DIVISION ACCORDING
TO A GIVEN RATIO
TRANSFER OF AN ANGLE
You may be required to divide a line into
parts so that the ratio between the whole
line and one of the parts is the same as
that between two other lines. A method
There is a geometric construction for
laying off, on another part of the same
drawing or on a different drawing, an angle
4-3