The most common
screws, and bolts.
Nails
There are many
fastening devices are nails,
types of nails—all of which
are classified according-to their use and form. The
standard nail is made of steel wire. The wire nail
is round-shafted, straight, pointed, and may vary
in size, weight, size and shape of head, type of
point, and finish. The holding power of nails is.
less than that of screws or bolts.
The COMMON WIRE nail and BOX nail
(fig. 6-83, view A) are the same, except that the
wire sizes are one or two numbers smaller for a
given length of the box nail than they are for the
common nail. The FINISHING nail (fig. 6-83,
view B) is made from finer wire and has a smaller
head than the common nail, Its head may be
driven below the surface of the wood, which
leaves only a small hole that is easily puttied. The
DUPLEX nail (fig, 6-83, view C) seems to have
two heads. Actually one serves as a shoulder to
give maximum holding power while the other
projects above the surface of the wood to make
withdrawal simple. The ROOFING NAIL (fig.
6-83, view D) is round-shafted and galvanized. It
has a relatively short body and comparatively
large head. Like the common wire, finishing, or
duplex nail, it has a diamond point.
Besides the general-purpose nails shown in
figure 6-83, there are special-purpose nails.
Examples include wire brads, plasterboard nails,
concrete nails, and masonry nails. The wire brad
has a needlepoint; the plasterboard nail has a
large-diameter flathead. The concrete nail is
specially hardened for driving in concrete. So is
the masonry nail, although its body is usually
grooved or spiraled.
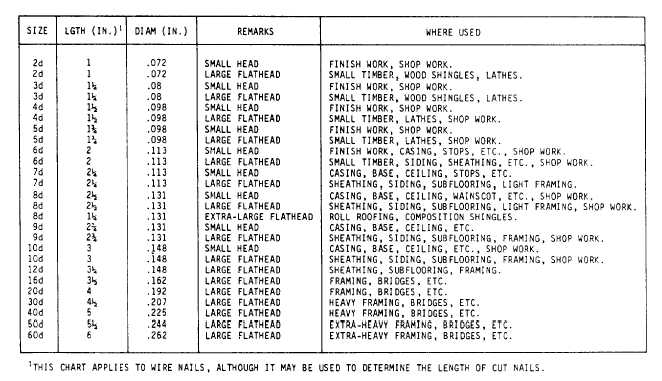
Lengths of wire nails NOT more than 6 in.
long are designated by the penny system, where
the letter d is the symbol for a penny. Thus, a 6d
nail means a sixpenny nail. The thickness of a wire
nail is expressed by the number, which relates to
standard wire gauge. Nail sizes (penny and length
in inches), gauges, and approximate number of
nails per pound are given in figure 6-83. Nails
longer than 6 in. (called SPIKES) are not
designated by the penny. The general size and type
of nail preferable for specific applications are
shown in table 6-4.
Table 6-4.-Size, Type, and Use of Nails
6-49