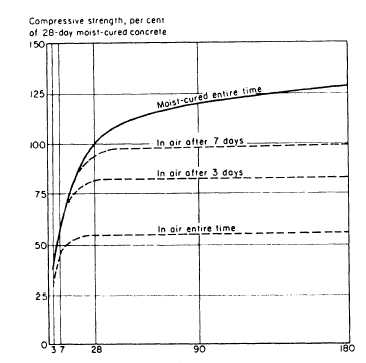
Figure 13-20.—Increase of concrete compressive strenth with
curing age.
figure 13-20. Note the long-time gain in strength that
occurs when proper temperature and moisture
conditions are maintained.
CONCRETE TESTING
Several tests, such as slump, air content, and weight
determination, are necessary to determine the quality of
freshly mixed concrete. In addition, strengths tests are
needed to determine whether a hardened concrete
satisfies specified strength requirements. This section
briefly discusses those tests.
Slump Test
As you know, the measure of the workability or
consistency of a concrete mix is its slump. With too little
slump, the mixture may be too difficult to work into the
forms and around the reinforcing steel. On the other
hand, with too much slump, the concrete ingredients
may segregate and excessive bleeding or migration of
water to the top surface of the freshly placed concrete
may occur. Excess bleeding increases the water-cement
ratio near the top surface of the concrete and results in
a weak top layer with poor durability.
To determine whether a freshly mixed concrete
satisfies the specified requirements for slump, you must
perform a slump test. By now, you should be thoroughly
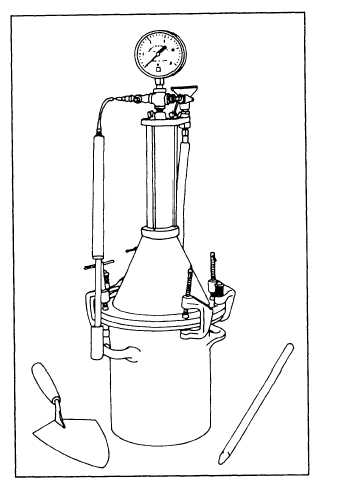
Figure 13-21.—Apparatus for air-content test.
familiar with the procedures of slump testing. If not, you
should review the discussion of slump testing that is in
the EA3 TRAMAN.
Air-Content Test (ASTM C 231)
An air-entraining admixture is added to the concrete
mix so that enough air will be entrained to improve
workability and durability of the mixture, but not
enough to reduce strength substantially. Air-entraining
cements may also be available for use in some military
situations. The desired amount of air is generally from
4.0 to 7.5 percent of the total mix.
The equipment for determining the percentage of
entrained air is included in the boxed test kit. The basic
tool is the pressure type of indicator, as illustrated in
figure 13-21. The equipment furnished in these kits
varies with the manufacturers. Each kit contains the
complete equipment for conducting the test, including a
detailed instruction pamphlet and the calibration
procedure for the particular meter. Before the air content
of a concrete mixture can be determined, the
13-29