and crushing targets. The dynamic overpressures cause
REVIEW QUESTIONS
damage by bending or dragging targets. Ship structures
and buildings are primarily vulnerable to static
Q5.
An airburst is a nuclear burst where the point
overpressures, whereas aircraft, masts, antennas, and
of detonation is below what altitude?
ex p o s e d p e r s o n n e l a r e v u l n e r a b l e t o d y n a m i c
overpressures.
1.
50,000 feet
2.
62,00 feet
UNDERWATER SHOCK
3.
80,000 feet
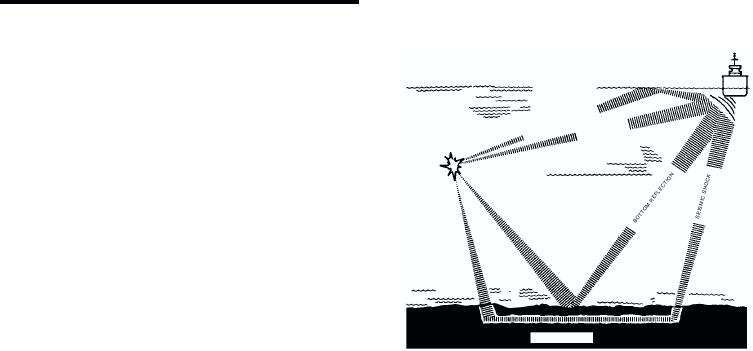
Underwater shock is the shock wave that is
4.
100,000 feet
produced in the water by an explosion. The shock wave
Q6.
A surface nuclear burst is a burst where the
initially travels several times the speed of sound in the
point of detonation is on or above the surface
water but quickly slows down to a hypersonic speed of
of the earth and the fireball touches the
approximately 5,000 fps. Underwater shock produces
surface of the earth.
rapid accelerations that can disarrange equipment and
machinery, rupture hulls, and/or injure personnel. Both
1.
True
the directly transmitted shock wave and the shock
2.
False
wave reflected from the sea bottom can be damaging.
An underwater explosion produces a shock wave
Q7.
An underwater nuclear burst produces
similar to that of an airburst. However, underwater
underwater shock and a water plume that then
causes a base surge.
shock damage is measured by the peak vertical
velocity (for surface ships) and by the peak
1.
True
translational velocity (for submerged submarines),
2.
False
rather than by the water overpressures produced by the
shock front. Figure 10-7 shows the direct and reflected
shock waves.
EFFECTS OF NUCLEAR WEAPON
BURSTS
OCEAN SURFACE
Learning Objective: Recall the different types of
ION
ECT
effects resulting from nuclear bursts.
EFL
ER
HOCK
FAC
CT S
SUR
DIRE
Specific effects of nuclear detonations depend on
EXPLOSION
the type of nuclear weapon and the type of burst. Also,
the effects are influenced considerably by the
environment in which the weapon is detonated. A
description of the effects of nuclear bursts and the
modification of these effects that can be caused by the
environment are provided in the following paragraphs.
AIR BLAST
OCEAN BOTTOM
Air blast is the shock wave that is produced in the
DCf1007
air by an explosion. The shock wave initially travels
outward at a velocity of approximately seven times the
Figure 10-7. Direct and reflected shock waves for an
speed of sound at high overpressures. It will then
underwater burst.
gradually slow down to a sonic speed of about
1,000 fps at low overpressures.
Four factors determine whether the greater
An air blast produces a rapid increase in the normal
damage will be caused by the direct wave or the
atmospheric (static) pressure and creates high wind
reflected wave:
(dynamic) overpressures. The high static
overpressures produced cause damage by squeezing
1. Distance from burst
10-5

