PROTECTIVE SHIELDING
REVIEW QUESTIONS
Protective shielding is one method of defense
Q7.
When is on-station monitoring conducted?
against nuclear radiation. The tremendous penetrating
1.
After cessation of fallout to report
power of gamma rays makes it difficult to provide
gamma intensities
enough shielding to protect personnel from gamma
rays. However, the structure of the ship provides some
2.
Before cessation of fallout to report
protection. The main materials likely to provide
gamma intensities
shielding aboard ship are steel plating, piping,
3.
After cessation of fallout to report
machinery, water, fuel oil, and perhaps wood.
alpha contamination
Shielding materials at shore facilities also include
concrete and earth.
4.
Before cessation of fallout to report
alpha contamination
The amount of shielding required to stop gamma
rays is measured in half-value layer thicknesses or
Q8.
Which survey is sometimes referred to as the
"half-thicknesses," for short. A "half-thickness" is
gross external survey?
defined as the amount of material necessary to cut
1.
Rapid external survey
down the amount of radiation to one-half of its original
value. The half-thickness for each material is different.
2.
Extensive external survey
For example, a concrete shield about 6 inches thick or
3.
Basic external survey
an earth shield about 7 1/2 inches thick will cut the
gamma radiation in half. Suppose that you are in a
4.
Precise external survey
p l a c e w h e r e t h e ga m m a r a d i a t i o n ex p o s u r e i s
Q9.
Which of the following terms best describes
400 roentgens. If you are behind a half-value layer
a type of survey that is recommended for
thickness at the time, you will receive a dose of
any area in which measured radiation
200 roentgens. Now suppose you are standing behind
dosages exceed predicted levels by more
two shields, each of which is a half-thickness. The
than 25 percent?
400 roentgens of gamma radiation is reduced to
200 roentgens by the first half-thickness and then to
1.
Simple survey
100 roentgens by the second half-thickness. With each
2.
Intensive survey
additional half-thickness shield, you reduce the
remaining gamma radiation by half. Remember that
3.
Detailed survey
these thicknesses do not stop gamma radiation
4.
Advanced survey
completely; instead, each cuts it in half. In a nuclear
attack, one half-thickness of steel or concrete might be
enough shield to keep you from getting a lethal dose of
gamma radiation.
RADIOLOGICAL EXPOSURE
CONTROL
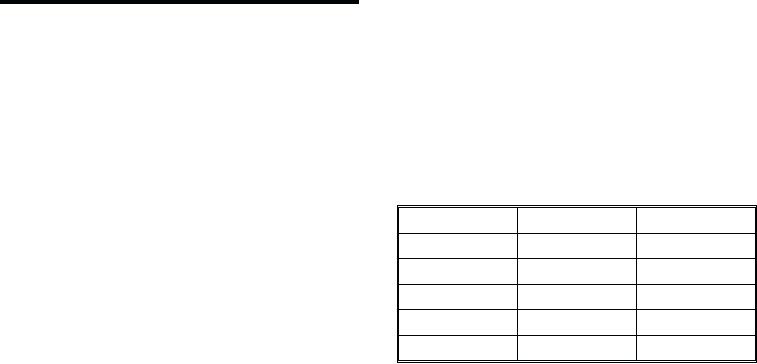
The estimated half-thicknesses of some materials
are shown below. Note that initial radiation is more
Learning Objective: Recall the different types of
penetrating than residual radiation and requires a
exposure control.
larger thickness to reduce the radiation to one-half of
its original value. These materials are listed in the order
Exposure control is the actions required to
of their effectiveness as shields against gamma
minimize the spread of contamination to personnel and
radiation.
the shipboard environment. The objective is to limit the
total dose received by individuals from both internal
and external sources and to minimize the transfer of
MATERIAL
INITIAL
RESIDUAL
contamination into the interior of the ship. Onboard
Steel
1.5 inches
0.7 inch
your ship you will have a chemical, biological, and
Concrete
6.0 inches
2.2 inches
radiological (CBR) defense bill, which will have
Earth
7.5 inches
3.3 inches
routes, used to minimize and control exposure. Other
means of exposure control are protective shielding,
Water
13.0 inches
4.8 inches
ready shelter and deep shelter, which will be described
Wood
23.0 inches
8.8 inches
in the following paragraphs.
11-13

