assemblies. The reticle has two cross hairs at right
angles to each other, and some models have stadia
hairs. The telescope and level bar assembly is
mounted on a spindle that permits the unit to be
revolved only in a horizontal plane. It cannot be
elevated or depressed. A clamp and tangent screw
acts on this spindle for small motions to permit
accurate centering. The spindle mounts in a
four-screw leveling head that rests on a foot plate.
The foot plate screws onto the threads on the
tripod. When the instrument is properly leveled
and adjusted, the line of sight, defined by the
horizontal cross hair, will describe a horizontal
plane.
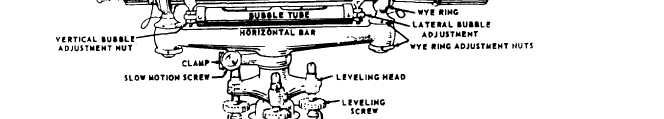
The two distinct types of engineer’s levels,
classified according to their support, are the wye
level and the dumpy level. The WYE LEVEL
(fig. 11-24) is so called because its telescope is
supported by a pair of wye rings. These rings can
be opened for the purpose of turning the telescope
or rotating it around its horizontal axis. The
bubble tube (vial) can be adjusted, either vertically
or laterally, by means of adjusting nuts at the ends
of the bubble tube. All these features are provided
for the purpose of making fine adjustments. The
DUMPY LEVEL (fig. 11-25) has its telescope
rigidly attached to the level bar, which supports
an adjustable, highly sensitive level vial. During
visual leveling operations and observations, both
types handle similar basic operations. Their cross
hairs are brought into focus by rotation of the
eyepiece, and their target, into clear focus by
rotation of the focusing knob. Their telescope can
be exactly trained on targets by lightly tightening
the azimuth clamp and manipulating the azimuth
tangent screw.
PRECISION LEVEL
Other types of leveling instruments have been
incorporated into the SEABEE units. In fact, the
self-leveling level has now become standard
Figure 11-24.-A wye level.
11-28