Q1.
Q2.
Q3.
Q4.
Q5.
Q6.
Q7.
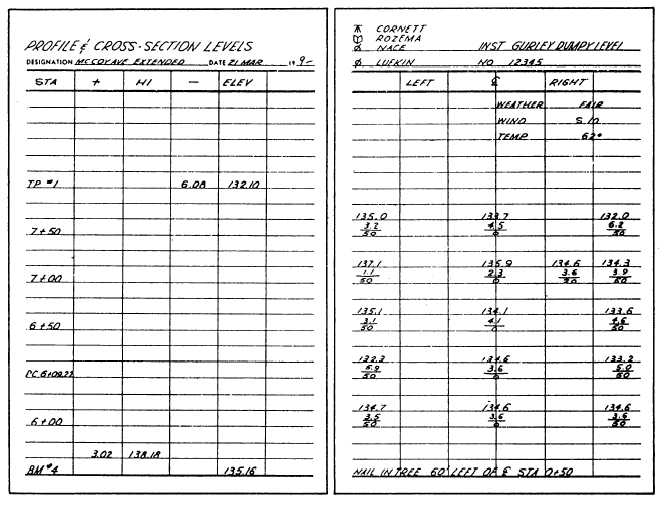
Figure 10-36.—Profile and cross-section levels.
QUESTIONS
Into what three phases are route surveys usually
broken?
For what reasons should overhead electrical
pole lines be located on the side of a street that
is most free from other lines and trees?
As it relates to the surface drainage of water,
what does the term “runoff” mean?
Refer to figure 10-3. What is the invert of the pipe
at station 1 + 50?
Refer to the field notes shown in figure 10-36.
Assuming the road is 30 feet wide, what is the (a)
area of the cross section at station 6 +00 and (b)
volume between stations 6 + 00 and 6 + 50?
As related to muss diagrams, what is the limit of
economic haul?
In which of the following ways does an as-built
survey performed for the purpose of verifying the
location of points as they are constructed in the
field differ from an as-built survey that is per-
formed for the purpose of monitoring construc-
tion progress?
a. The amount of time allowed to perform the
survey
b. The equipment used to perform the survey
c. The degree of accuracy required
Q8. When staking out a sewer line, at what interval
of distance should you usually set the center-line
stakes or the offset hubs?
Q9. Refer to figure 10-29. What is the sine of the
anglee that you should turn from station 10 +
38.83 to locate pile No. 8?
Q10. In land surveying, when a metes-and-bounds
description is being prepared, what may be
added to the bearings of the boundary lines to
help in retracing the lines?
10-37