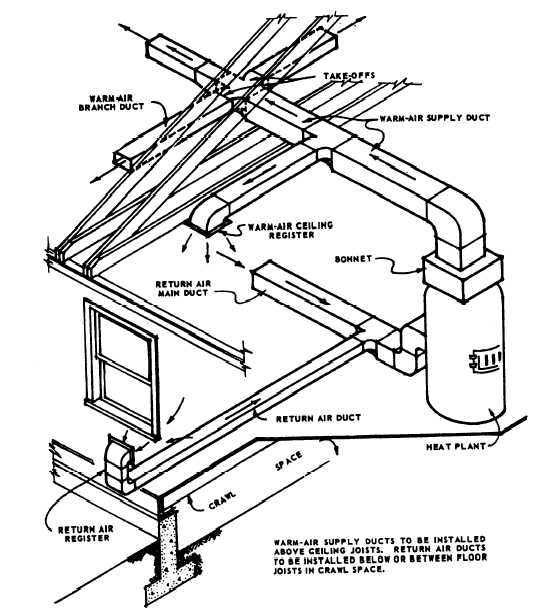
Figure 4-5.—Forced-air heating system.
following paragraphs. For a discussion of heating
principles (including theory, measurement of heat, and
heat transfer) and a discussion of the principles of refriger-
ation and air conditioning, you should read chapters 9
and 10 of Utilitiesman 3, NAVEDTRA 12532.
HEATING SYSTEM
The purpose of designing and installing a heating
system in a building is to provide proper heat
distribution to the various rooms or zones within the
building. This can be done by means of various types of
heating systems.
Warm-Air Furnace Systems
A warm-air furnace can be any type of heating
device that circulates warmed air to locations where it
is needed. One type, the wall heater, draws in cold air
near the floor, passes the air over a heating unit, and then
exhausts the warmed air to heat the surrounding area
Another type is the gravity warm-air furnace. It is a
direct-fired furnace that transfers heat by convection In
other words, warmed air circulating through the furnace
rises through ductwork to the areas to be heated and
then, as the air cools, it descends to the furmace to be
reheated Since the installation of this type of system
requires abasement and large, unsightly ductwork, it is
seldom used in new construction.
A more commonly used type of warm-air furnace is
the forced-air furnace (fig. 4-5). In this type, an oil or
gas burner heats the fins of a heat exchanger. The heat
exchanger warms the cool air passing over it. The
warmed air is then forced, by fan, through relatively
4-5