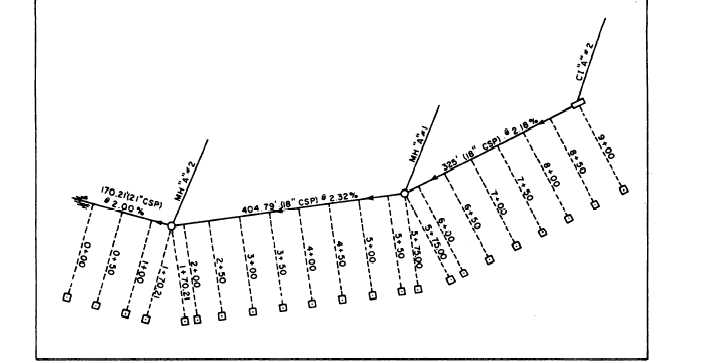
station where you will set a hub. Consider fig-
ure 10-19, for example. This is a plan showing a line
running from a curb inlet through two manholes to an
outfall. The dotted lines are offsets (greatly
exaggerated for clearness) to points where you will set
the hubs. Note that at stations 5 + 75 and 1 + 70.21,
you set two hubs, one for the invert in and the other
for the invert out.
The invert elevations at the manhole (MH) are
given on the profile. Suppose that the invert out at CI
“A” #2 is 122.87 feet. The gradient for this pipe is 2.18
percent. Station 8 + 50 lies 0.50 station from CI “A”
#2; therefore, the invert elevation at station 8 + 50 is
122.87 feet minus (0.50 x 2.18), or 122.87 feet minus
1.09, or 121.78 feet. You compute the invert
elevations at the other intermediate stations in the
same manner.
Suppose now that you are starting the stakeout at
CI “A” #2. The final-location party left a center-line
stake at this station. You occupy this point, turn 90
degrees left from the line to MH “A” #1, and measure
off the offset; for example, 8 feet. This is presuming
that, if the ground slopes across the line, the high side
is the side on which the hubs are placed in figure
10-19. Hubs are always placed on the high side to
prevent them from being covered by earth dozed off
to form a bench for the trench-digging rig.
You drive a hub 8 feet offset from station 9 + 00
and determine the elevation of the top of the hub. The
vertical distance from the top of the hub to the invert
at station 9 + 00 is the difference between the invert
elevation and the elevation of the top of the hub. The
invert elevation at station 9 + 00 is 122.87 feet.
Suppose the elevation of the top of the hub is 126.94
feet. Then you would mark the guard stake for this
hub, CI “A” #2 inv. C 4.07´. Suppose the elevation of
the top of the hub driven at station 8 + 50 is 127.33.
The invert elevation at this station is 121.78; therefore,
you would mark the guard stake for this station, 8 +
50, C 5.55´.
The manner in which the construction crew will
use these hubs to dig the trench to grade will vary
according to the preference of the supervisor for one
of several methods. One method involves the erection
of a batter board across the trench at each hub. The top
of each board is placed on the posts at a set distance
above invert elevation; for example, 10 feet. Fig-
ure 10-20 illustrates this method.
Take station 9 + 00 in figure 10-19, for example.
The elevation of the top of the hub is 126.94 feet and
the invert elevation is 122.87 feet. To be 10 feet above
invert elevation, the top of the batter board must be
placed on the post 5.93 feet above the top of the hub.
To get this distance, the field constructor would simply
Figure 10-19.—Sewer stakeout plan.
10-20