weight, (2) the effect of free surface, and (3) the effect
When a ship has trim, however, neither the draft
of free communication.
amidships nor the average of the forward and after
drafts will give a true mean draft. For most types of
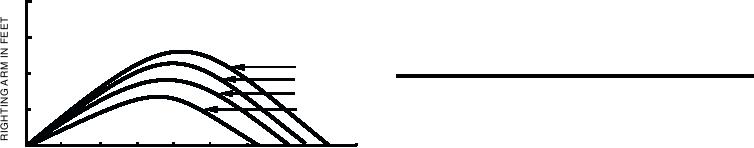
Figure 12-32 shows the development of a stability
ships, the curves of form may be used without
curve with corrections for added weight, free surface,
correction for trim, PROVIDED the trim is less than
and free communication. Curve A is the ship's original
about 1 percent of the length of the ship. When the trim
stability curve before flooding. Curve B represents the
is greater, however, the readings obtained from the
situation after flooding; this curve shows the effect of
curves of form must be corrected for trim.
added weight (increased stability) but it does NOT
s h ow t h e e ff e c t s o f f r e e s u r fa c e o r o f f r e e
Longitudinal stability is the tendency of a ship to
communication. Curve C is curve B corrected for free
resist a change in trim. The longitudinal metacentric
surface effect only. Curve D is curve B corrected for
height multiplied by the displacement is taken as a
both free surface effect and free communication effect.
measure of INITIAL longitudinal stability when trim
Curve D, therefore, is the final stability curve; it
is very small. (It is important to note that the
incorporates corrections for all three effects of loose
longitudinal metacenter (M1) is NOT the same as the
water.
transverse metacenter.) A more accurate measure of
the ship's ability to resist a change of trim is made in
terms of the moment required to produce a change in
trim of a definite amount. The MOMENT TO
4
CHANGE TRIM 1 INCH (MTI) is used as the standard
3
measure of resistance to longitudinal inclination.
CURVE B
2
CURVE A
REVIEW QUESTIONS
CURVE C
CURVE D
1
Q7.
The ship's center of gravity is the point at
0
50
20
10
60
90
30
40
70
80
which all weights of the ship may be
ANGLE OF HEEL IN DEGREES
considered to be concentrated. The force of
DCf1232
gravity is considered as acting straight
downward, through the center of gravity, at
Figure 12-32. Development of stability curve corrected for
effects of added weight, free surface, and free communication.
right angles to the waterline.
1.
True
LONGITUDINAL STABILITY
2.
False
Q8.
Detailed information concerning changes in
Thus far in studying stability, you have been
the center of gravity of a ship can be obtained
concerned only with TRANSVERSE STABILITY and
from which of the following NSTMs?
with TRANSVERSE INCLINATIONS. LONGI-
T U D I NA L S TA B I L I T Y a n d L O N G I T U D I NA L
1.
NSTM, chapter 096
I N C L I N AT I O N S , o r T R I M , s h o u l d a l s o b e
2.
NSTM, chapter 040
considered.
3.
NSTM, chapter 033
Trim is measured by the difference between the
forward draft and the after draft. When the after draft is
4.
NSTM, chapter 010
greater than the forward draft, the ship is said to be
Q9.
Which of the following terms is used to
TRIMMED BY THE STERN. When the forward draft
describe water or other liquid that has a free
is greater than the after draft, the ship is said to be
surface?
TRIMMED BY THE BOW or TRIMMED BY THE
HEAD. As a ship trims, it inclines about an athwartship
1.
Reserve buoyancy
axis that passes through a point known as the CENTER
2.
Reserve ballast
OF FLOTATION (CF).
3.
Draft
The mean draft that is used to enter the draft scale
4.
Loose water
to read a displacement curve is the draft amidships.
12-19

