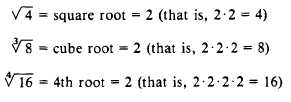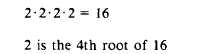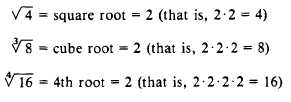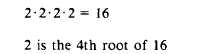PROTRACTOR—Instrument used for measuring
and laying off angles.
PYRAMID—A figure having a plane polygon for
its base and triangles meeting at a common vertex
for its sides.
PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM—A law of
mathematics that states that the square of the
hypotenuse of a right triangle equals the sum of
the squares of the other two sides.
QUADRILATERAL—A polygon bounded by
four sides.
QUALITATIVE CHART OR GRAPH—Any
chart that emphasizes the relationships of facts.
QUANTITATIVE CHART OR GRAPH—A
chart or graph that emphasizes numerical values.
RADIAN—A system for measuring angles where
2n radians equals 360°; 1 radian = 57.3°.
RADICAL—A symbol placed on a mathematical
quantity to indicate the root of the quantity; for
example.
RADIUS-A straight line from the center of a
circle or sphere to its circumference or surface.
RATIO-A comparison of two like quantities; for
example, 2/3, 2:3.
RATIONAL NUMBER—A number that can be
expressed as the quotient or ratio of two whole
numbers: Fractions 2/7, Integers 3/1 = 3. A
radical is a rational number if the radical is
removable; for example, ~ = 2, @ = 3.
REAL NUMBERS—All positive and negative
numbers.
RECIPROCAL—The reciprocal of
equals 1 divided by the number.
RECTANGLE—A parallelogram
adjacent sides join at right angles.
a number
in which
RECTANGULAR PRISM—A solid figure whose
base is a rectangle.
REFERENCE PLANE—The normal plane from
which all information is referenced.
REGULAR POLYGON—An equilateral polygon.
RESIDUAL SOIL—Any soil that results from
weathering in place and that is not moved from
its place of origin.
RETICLE—A system of wires, hairs, threads,
etched lines, or the like, placed normal to the axis
of a telescope at its principal focus by means of
which the telescope is sighted on a star, or target,
or by means of which appropriate readings are made
on some scale, such as a leveling or stadia rod.
REVERSE CURVE—See OGEE CURVE.
REVISION BLOCK—Block drawn in the upper
right corner of construction drawings; contains
chronological list of all changes or revisions to
the drawing.
REVOLUTION—Object is projected on one or
more of the planes of projection but rather than
being in the normal position, it is revolved on an
axis perpendicular to one of the regular planes;
used when it can show the features of an object
more clearly than a normal orthographic projection.
REVOLVED SECTION—A sectional view used
to show the internal structure of an item within
the normal orthographic view.
RHOMBOID—A nonequilateral parallelogram in
which adjacent sides join at oblique angles.
RHOMBUS—An equilateral parallelogram in
which adjacent sides join at oblique (other than
right) angles.
RIGHT ANGLE—An angle of 90°.
ROOT—The number of times a quantity is found
as an equal factor within another quantity; for
example.
$%= 4th root of 16 = 2
AI-12