CHAPTER 5
DRAFTING: PROJECTIONS
AND SKETCHING
This chapter deals with the theory of
projections and methods of preparing projection
drawings. By applying basic geometric con-
struction (described in the preceding chapter) to
the various projection methods, you should be
able to clearly represent any given object or
structure on paper. Although the methods
discussed here are basic to all drawings, they are
easily adapted to construction drawings. This
chapter also covers various techniques of freehand
sketching. You will learn how to prepare quick
sketches to convey or develop your ideas.
Every object or structure you draw has length,
width, and depth, regardless of its size. However,
you must draw the object or structure on paper,
which is a flat two-dimensional plane. To show
the three dimensions by lines alone, you must use
either a system of related views or a single
pictorial projection. You must be able to show
clearly the shape of the object, give the exact size
of each part, and provide necessary information
for constructing the object.
In theory, projection is done by extending lines
of sight (called projection lines) from the eye of
the observer, through lines and points of an
object being viewed, to the plane of projection.
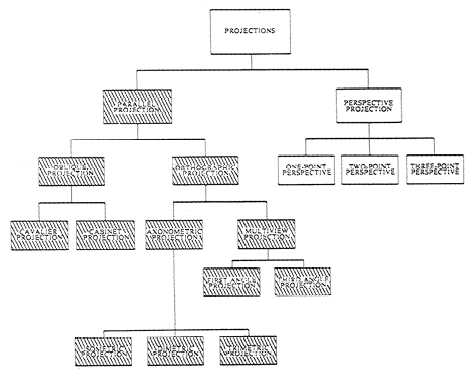
PARALLEL PROJECTION
To satisfy requirements for preparing single-
or multi-view drawings, you may use two main
types of projection: PARALLEL and PER-
SPECTIVE (fig. 5-1). PARALLEL projection
Figure 5-1.—Classification of major projections.
5 - 1