4.16
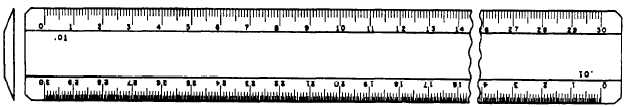
Figure 2-26.-Flat metric scale.
Metric Scale
The METRIC SCALE is used in the
place of the architect’s and the engineer’s
scale when measurements and dimensions are in
meters and centimeters. Metric scales are
available in flat and triangular shapes. The
flat 30-cm metric scale is shown in figure 2-26.
The top scale is calibrated in millimeters
and the bottom scale in half millimeters. The
triangular metric scale has six fully divided
scales, which are 1:20, 1:33 1/3, 1:40, 1:50, 1:80,
and 1:100.
When you are using scales on a drawing, do
not confuse the engineer’s scale with the metric
scale. They are very similar in appearance.
Whenever conversions are made between the
metric and English system, remember that 2.54
cm equals 1 in.
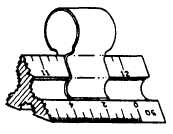
Triangular Scale Clip
For use with a triangular scale, a scale clip or
scale guard, such as the one shown in figure 2-27,
is very helpful. The clip makes it easy for you to
identify what scale you are using. Large spring-
type paper clips will serve the same purpose when
scale clips are not available.
29.276
Figure 2-27.-Use of triangular scale clip.
MAP MEASURES AND
SCALE INDICATORS
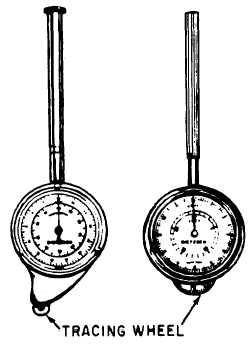
MAP MEASURES are precision instruments
for measuring the lengths of roads, pipelines, and
other irregular outlines on maps and drawings.
Distances are measured by first setting the
instrument to zero, then tracing the line to be
measured with the small, projecting tracing wheel,
like that on the map measures shown in figure
2-28.
In using map measures, do not depend entirely
on the indicated numerical scale. Always check
it against the graphical scale on the map or
drawing. Verify if, for example, 1 in. traversed
45.712X
Figure 2-28.-Types of map measures.
2-21