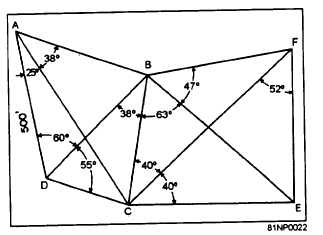
Figure 2A
IN ANSWERING QUESTIONS 2-8 THROUGH 2-11,
USE THE CHAIN OF QUADRILATERALS IN FIGURE
2A AND THE TABLES IN APPENDIX II.
2-8.
The size of the angle ABD is
1.
37°
2.
51°
3.
57°
4.
60°
2-9.
What is the length of the line DB?
1.
500 ft
2.
531 ft
3.
548 ft
4.
554 ft
2-10.
What is the length of line CE?
1.
646 ft
2.
608 ft
3.
697 ft
4.
709 ft
2-11.
What is the length of line BF?
1.
452 ft
2.
487 ft
3.
520 ft
4.
561 ft
Learning Objective: Identify the
construction and uses of various
targets and signals as related to
triangulation.
2-12.
What minimum number of reference
markers must be used for triangu-
lation stations of first-order
precision?
1.
One
2.
Two
3.
Three
4.
Four
2-13.
What is the difference between a
primary triangulation station and
a secondary triangulation station?
1.
The secondary station is used
as a control point; the primary
station is not
2.
The secondary station is an
instrument station; the primary
station is not
3.
The primary station is an
instrument station; the
secondary station is not
4.
The primary stations are set
up on monuments only; the
secondary stations can use any
point
2-14.
A tripod target is the most satis-
factory target to use because of
which of the following qualities?
1.
Its accuracy
2.
Its durability
3.
Its ease of construction
4.
Each of the above
2-15.
One of the disadvantages of using
a bipod target is that it
1.
is difficult to transport
2.
must be strongly guyed
3.
is extremely difficult to
construct
4.
cannot be used when first-
or second-order precision
is required
2-16.
For accuracy, you should perform
first- and second-order triangu-
lation surveys (a) during what time
of day and (b) using what type of
signals?
1. (a) At night
(b) signal lights
2. (a) At night
(b) heliotropes
3. (a) In daylight
(b) target sets
4. (a) In daylight, while overcast
(b) nonilluminating bipod
signals
Learning Objective: Identify the
procedures used in triangulation
surveying and recognize their
importance.
9