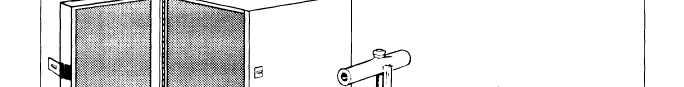
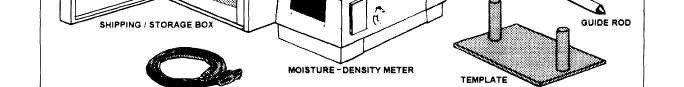
Figure 13-7.—Nuclear moisture-density meter.
moisture-density meter, such as the one illustrated in
and receive certification through the Naval
figure 13-7.
The meter contains sealed radioactive materials,
typically cesium and a combination of americium mixed
with beryllium powder. The cesium emits gamma
radiation that the detector in the meter can count when
it is passed through the soil. This count can be translated
to density. The americium, interacting with the
beryllium, emits neutrons following collision with
hydrogen that are moderated and detected by the meter.
The moisture content can be determined by measuring
the hydrogen concentration in the soil.
When you are using the moisture-density meter,
counts or readings are obtained and used with a
calibration chart to determine the wet density and
moisture content. The dry density is computed from the
wet density.
CAUTION
Before using the nuclear moisture-density
meter, you must complete specialized training
Construction Training Center at either Gulfport,
Mississippi, or Port Hueneme, California.
BEARING TESTS
The bearing capacity of a soil is expressed in terms
of shear resistance, which means the capacity of the
load-bearing portion of a material or member to resist
displacement in the direction of the force exerted by the
load.
There are various types of load-bearing tests. For
description purposes we will briefly discuss the
California bearing ratio (CBR) test.
The California bearing ratio is a measure of the
shearing resistance of a soil under carefully controlled
conditions of density and moisture. The CBR is
determined by a penetration shear test and is used with
empirical curves for designing flexible pavements.
The test procedure used to determine the CBR
consists of two principal steps. First, the soil test
13-10