motorized) type of jack. Three proving rings are
available with capacities of 2,000, 5,000, and 7,000
pounds, respectively. The surcharge weights are used to
approximate (within + 5 pounds) the expected weight of
the pavement and base in the field. The tripod
attachment (when fitted with a dial indicator) and the
swell plate are used to measure the expansion, or swell,
of the material in the CBR mold. Other items needed to
perform the test are equipment and tools, such as a
balance or scale, a CBR mold, a 10-pound tamper,
mixing bowls, spoons, spatulas, a soaking tank or
bucket, and moisture canisters.
Preparation of Test Samples
When a bearing-ratio test is made of a compacted
sample, you will use the 6-inch-diameter CBR mold
with a 2 1/2-inch spacer disk in the mold beneath the
sample. The use of the spacer reduces the depth of the
sample to 4 1/2 inches. The use of another size spacer
will result in volume and compactive effort changes that
may not meet ASTM or other recognized standards for
the CBR test.
The method of preparing the test specimens and the
number of specimens depend upon such factors as the
type of airfield or road and the soils encountered at the
site. The soil sample should be tested in the laboratory
at a density comparable to the density required at the
construction site. There are situations where moisture
conditions are favorable and the subgrade will not
accumulate moisture approaching a saturated condition.
In these cases, samples should be tested at a moisture
content that approximates actual moisture conditions
expected during the time the road or airfield is used. In
all other conditions, the samples are laboratory tested in
a saturated condition.
The saturated condition is attained by soaking the
sample. First, place the sample in the mold and compact
it. The compactive effort used and the number of
compacted samples required depend upon the soil type,
weight and type of field compaction equipment, and
other job conditions. Normally, compactive efforts of
12, 26, and 55 blows per layer (for five layers) are used
in each of three successive compaction tests. The
10-pound tamper is used for compacting the samples.
After compacting the sample, trim it and remove the
base plate and spacer disk. Then place a piece of filter
paper over the trimmed or struck-off top of the sample
and place the base plate over this top. Turn the mold over
and set it in a bucket on the base plate. The bottom of
the sample, which was next to the spacer disk during
compaction, is now uppermost. Apply the appropriate
13-12
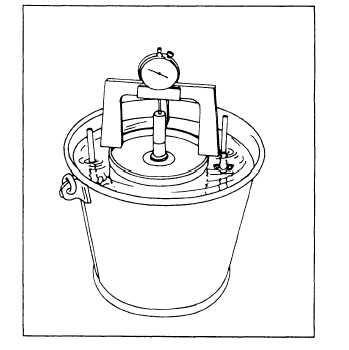
Figure 13-10.—Apparatus for soaking a CBR test sample.
number of surcharge weights needed to approximate the
expected in-place weight of the pavement and base. One
5-pound surcharge weight is equivalent to 3 inches of
overlying material. Then set in place the tripod
attachment, dial, and swell plate, as shown in figure
13-10.
Immerse the mold and the sample in water in the
bucket and leave them to soak for about 4 days. An initial
reading of the tripod dial is made when the sample is
first placed in the water. Then, at the end of the soaking
period, the dial is read again to determine the amount of
swell. A swell in excess of 3 percent of the initial height
of the specimen is considered to be excessive. After
making the final reading of the dial, you remove the
sample and mold from the water and allow them to drain
for about 15 minutes before conducting the penetration
test.
Penetration Test
In the penetration test, the bearing capacity of a soil
is determined by measuring the extent to which the
sample, placed in a mold, is penetrated by a penetration
piston. The sample (in the CBR mold) is placed in the
loading press, as shown in figure 13-9. The piston is
placed on top of the material, and a proving ring is
placed between the top of the piston and the top of the
loading press.
As the jack is cranked upward, the dial in the center
of the proving ring records the pressure being applied to