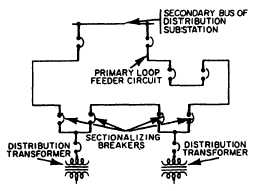
Figure 2-4.—Loop (or ring) distribution system.
connected directly to distribution centers. This
eliminates the need for substations because the
generator generates a usable voltage.
Primary Feeders
Primary feeders are those conductors in a distribu-
tion system that are connected from the distribution sub-
stations and that transfer power to the distribution
centers (fig. 2-2). They may be arranged as radial, loop, or
network systems and may be overhead or underground.
RADIAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM.— A
schematic example of a radial distribution system is
shown in figure 2-3. In this system, primary feeders take
power from the distribution substation to the load areas
by way of subfeeders and lateral-branch circuits. This is
the most common system used because it is the simplest
and least expensive to build. It is not the most reliable
system, however, because a fault or short circuit in a
main feeder may result in a power outage to all the users
served by the system.
Service on this type of system can be improved by
installing automatic circuit breakers that will reclose the
service at predetermined intervals. If the fault continues
after a predetermined number of closures, the breaker
will be locked out until the fault is cleared and service
is restored.
PRIMARY LOOP (OR RING) DISTRIBUTION
SYSTEM.— The loop (or ring) distribution system is
one that starts at a distribution substation, runs through
or around an area serving one or more distribution
transformers or load centers, and returns to the same
substation. The loop system (fig. 2-4) is more expensive
to build than the radial type, but it is more reliable and
may be justified in areas where continuity of service is
required—at a medical center, for example.
In the loop system, circuit breakers sectionalize the
loop on both sides of each distribution transformer
connected to the loop. A fault in the primary loop is
cleared by the breakers in the loop nearest the fault, and
power is supplied the other way around the loop without
interruption to most of the connected loads. If a fault
occurs in a section adjacent to the distribution
substation, the entire load can be fed from one direction
over one side of the loop until repairs are made.
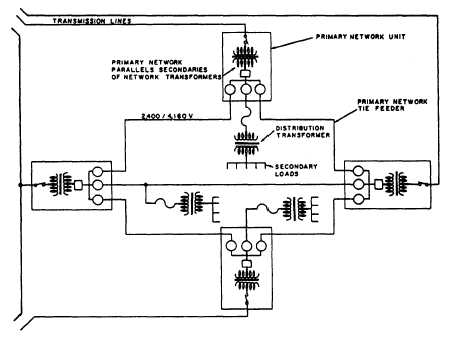
NETWORK SYSTEM.— The network system
(fig. 2-5) is the most flexible type of primary feeder
Figure 2-5.—Network distribution system.
2-3