naval ships that could use that method of sewage
pollution control without serious reduction in military
capabilities. The CHT system represented the least cost
and risk solution to the problem. Most operational fleet
ships of sufficient size have CHT systems.
Navy ships have two types of CHT systems. The
type for a particular ship depends on the holding tank
capacity. Systems with tanks with a capacity of more
than 2000 gallons use a comminutor and aeration
system. Smaller systems with capacities of less than
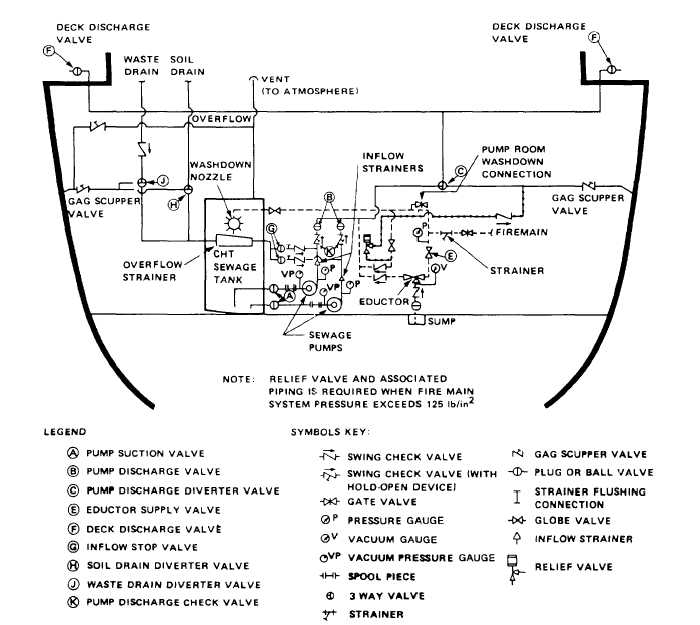
2000 gallons use strainers. Figures 6-2 and 6-3 show the
comminutor-type and the strainer-type systems.
The goal for the CHT system is to provide the
capacity to hold shipboard sewage generated over a
12-hour period. Large ships can usually reach the goal,
but smaller ships often reach their capacity in about 3
hours; probably not enough time to get outside the
3-mile restricted zone. Ships can get a waiver if they
cannot reach the 12-hour holding time because of
serious impact on military or operational
characteristics. These ships are identified in DOD
Directive 6050-4 of April 1976. Chapter 997 of Naval
Ships’ Technical Manual discusses sewage discharge
procedures for ships in drydock.
Figure 6-3.–Strainer-type CHT system
6-5