shaft assembly, and the motor. Within the striker
assembly, an eccentric controls the movements of a
spring-driven hammer. The striker operates as a piston
and strikes the diaphragm at a frequency governed by
motor speed. The eccentric shaft assembly is a bearing-
mounted shaft connected through an eccentric and ball-
and-socket arrangement to the striker assembly. The
eccentric shaft is rotated by a V-belt driven by the 1-1/2
horsepower, 240 Vdc motor. The motor receives its
controlling voltage from the power converter unit
(PCU) on board the ship.
ACOUSTIC POWER CABLE
(BUOYANT)
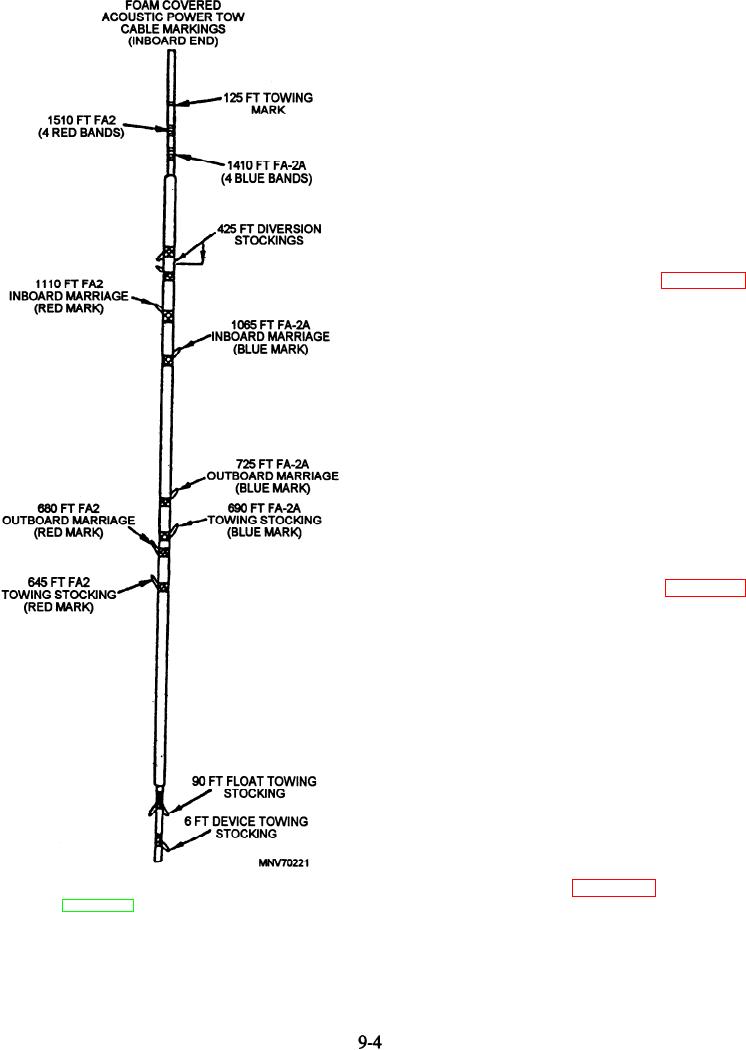
The acoustic power cable (APC) Acoustic-Power-Cable-180.html">(figure 9-4)
provides electrical power to operate acoustic devices at
an extended distance from the ship, contributing to the
ship's safety during minesweeping operations. It
contains four conductors, and is 1,650 feet long and
1-1/2 inches in diameter. It has two nonbuoyant
sections, 125 feet on the outboard end and 250 feet on
the inboard end. The buoyant section is 1,275 feet long
and 3 inches in diameter. Polyethylene foam wrapped
around the power cable provides the necessary
buoyancy.
AUTOMATIC CONTROLUNIT
SG-1224A/SLQ-37(V)
The automatic control unit (ACU) (figure 9-5)
provides the waveforms used for acoustic and magnetic
mine countermeasures.
are converted to direct current by the power converter
unit (PCU) and applied through the APC to run the
motors in the TB-26 and the TB-27. Magnetic voltage
waveforms provided by the ACU are sent to the ship's
magnetic minesweeping generators, converted to high-
amperage current, and applied to the ship's magnetic
tail.
FLOATS
Minesweeping floats (figure 9-6) are used to
support either minesweeping otters or acoustic devices

