FRACTURE OF THE SPINE
The spinal cord, which contains nerve fibers in
direct connection with the brain, is enclosed and
protected by a bony structure known as the SPINAL
COLUMN, or BACKBONE. The spinal column is
made up of a number of small bones called the
VERTEBRAE.
If the spine is fractured at any point, the spinal cord
may be crushed, cut, or otherwise damaged so severely
that death or paralysis can result. However, when the
fracture occurs in such a way that the spinal cord is not
seriously damaged, there is a good chance of complete
recoveryPROVIDED THE VICTIM IS PROPERLY
CARED FOR. Any twisting or bending of the neck or
back whether due to the original injury or caused by
careless handling later, is likely to cause irreparable
damage to the spinal cord.
The primary symptoms of a fractured spine are pain,
shock and paralysis. PAIN is likely to be acute at the
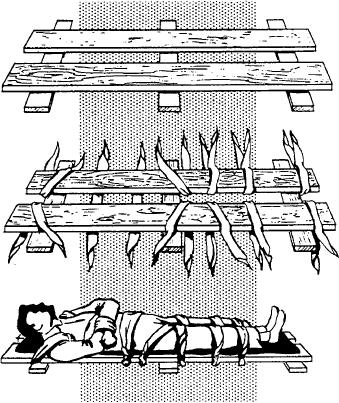
Figure 10-55.--Improvised frame for transporting victim with
point of fracture. It may radiate to other parts of the body.
fractured spine.
SHOCK is usually severe, but (as in all injuries) the
symptoms may be delayed for sometime. PARALYSIS
occurs when the spinal cord is seriously damaged. When
When it is necessary to transport a person who has
the victim is unable to move his legs, feet, or toes, the
suffered a fracture of the spine, follow these general
fracture is most probably in his back When he cannot
rules:
move his fingers, his neck is probably broken.
Remember, however, that a spinal fracture does not
1. If the spine is broken at the NECK, the victim
always injure the spinal cord, so the victim is not always
must be transported lying flat on his back with his face
up. Place pillows or sandbags beside his head so it
paralyzed. Any person who has acute pain in the back
or neck following an injury, should be treated as though
cannot be turned to either side. DO NOT PUT
a fracture of the spine has occurred. This remains true
PILLOWS OR PADDING UNDER HIS NECK OR
even though no other symptoms are present.
HEAD.
TREATMENT. First aid for all spinal fractures,
2. When you suspect the spine is fractured but do
whether of the neck or bath has two primary purposes:
not know the location of the break treat the injury as
(1) to minimize shock and (2) to prevent further injury
though the victim has a broken neck. In other words, the
to the spinal cord.
victim should be lying on his back with his face up.
When both the neck and back are broken, treat the victim
You must keep the victim comfortably warm. Do
in the same manner; that is, keep the victim on his back
NOT attempt to place the victim in the position normally
with his face up.
used to treat shock. Any unnecessary movement may
3. No matter where the spine is broken, USE A
cause further injury to the spinal cord. Keep the victim
lying flat. Do NOT attempt to lower the victim's head.
FIRM SUPPORT IN TRANSPORTING THE VICTIM.
Use a rigid stretcher, or use a door, shutter, wide board,
To avoid further damage to the spinal cord, DO
or a frame similar to that shown in figure 10-55. Pad the
NOT MOVE THE VICTIM UNLESS IT IS
support carefully, and put blankets both under and over
ABSOLUTELY ESSENTIAL. But if you must transport
the victim. Use cravat bandages or strips of cloth to
the victim, DO NOT BEND OR TWIST HIS BODY;
fasten the victim firmly to the support.
DO NOT MOVE HIS HEAD FORWARD,
4. Hold the injured person by his clothing; then
BACKWARD, OR SIDEWAYS; AND DO NOT,
slide or pull the victim onto the support. DO NOT
UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES, ALLOW HIM TO
ATTEMPT TO LIFT THE VICTIM UNLESS YOU
SIT UP.
10-39

