then cover the victim with alight blanket and move him
without acclimatization and proper training. Excessive
into a warmer area). When the victim is conscious, give
sweating may result in painful heat cramps in the
him a solution of 1 teaspoon of salt dissolved in a quart
muscles of the abdomen, legs, and arms. Heat cramps
of cool water. If the victim vomits, do not give him any
may also result from drinking ice water or other cold
more fluids. Transport the victim to a medical facility as
drinks either too quickly or in too large a quantity after
exercise. Muscle cramps are often an early sign of
soon as possible.
approaching heat exhaustion. Muscle spasms or heat
cramps usually last only a few minutes and disappear
HEATSTROKE
spontaneously.
TREATMENT. To provide first-aid treatment for
Sunstroke is more accurately called heatstroke since
heat cramps, move the person to a cool place. Since heat
it is not necessary to be exposed to the sun for this
cramps are caused by loss of salt and water, give the
condition to develop. It is a less common but far more
victim plenty of water to drink adding about 1 teaspoon
serious condition than heat exhaustion since it carries a
of salt to a quart of water. Apply manual pressure to the
20-percent mortality rate. The most important feature of
cramped muscle, or gently massage the muscle to
heatstroke is the extremely high body temperature
relieve the spasm. In the event that the heat cramps do
(105F [41C] or higher) that accompanies it. In
not pass or become more severe, other symptoms may
heatstroke, the victim has a breakdown of his sweating
follow and the victim should be treated as a heat
mechanism and is unable to eliminate excessive body
exhaustion casualty and then transferred to a medical
heat. When the body temperature rises too high, the
facility for treatment.
brain, kidneys, and liver may be permanently damaged.
Sometimes the victim may have preliminary
HEAT EXHAUSTION
symptoms, such as headache, nausea, dizziness, or
weakness. Breathing is deep and rapid at first; later, it is
shallow and almost absent. Usually the victim is flushed,
Heat exhaustion is the most common condition
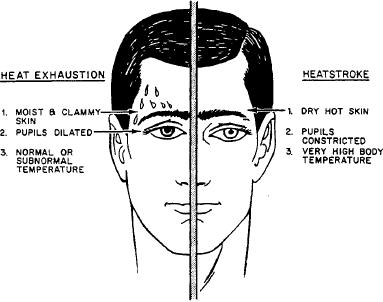
very dry, and very hot. His pupils are constricted
resulting from exposure to hot environments. Heat
(pinpointed) and the pulse is fast and strong. See figure
exhaustion can be a combination of several entities and
10-43 for a comparison of these symptoms with those
is, therefore, not an easy condition to diagnose. Because
of heat exhaustion.
of different causes, for example, water depletion or salt
depletion or a combination of both, the signs and
TREATMENT. When providing first aid for
symptoms vary.
heatstroke, keep in mind that this is a true life and death
emergency. The longer the victim remains overheated,
As a general rule, heat exhaustion involves a serious
the more likely he is to suffer irreversible body damage
disturbance of blood flow to the brain, heart, and lungs
that may cause the victim to experience weakness,
fatigue, headache, loss of appetite, and nausea. He may
faint but will probably regain consciousness when his
head is lowered to improve the blood supply to his brain.
The victim appears ashen gray; his skin is cold, moist,
and clammy; and the pupils of his eyes are dilated
(enlarged). The vital signs are usually normal; however,
the victim may have a weak pulse, together with rapid
and shallow breathing. The body temperature may be
below normal. Heat exhaustion is a complex malady and
is often misdiagnosed, even by medical personnel. You,
as a first-aider, should treat prolonged heat cramps and
any heat injury that is obviously not heatstroke as heat
exhaustion.
TREATMENT. Care for the victim as if he were in
shock Move the victim to a cool or air-conditioned area
Loosen clothing, applying cool wet cloths to the head,
axilla, groin, and ankles, and fan the victim. Do not
Figure 10-43.--Symptoms of heatstroke and heat exhaustion.
allow the victim to become chilled (if this does occur,
10-26

