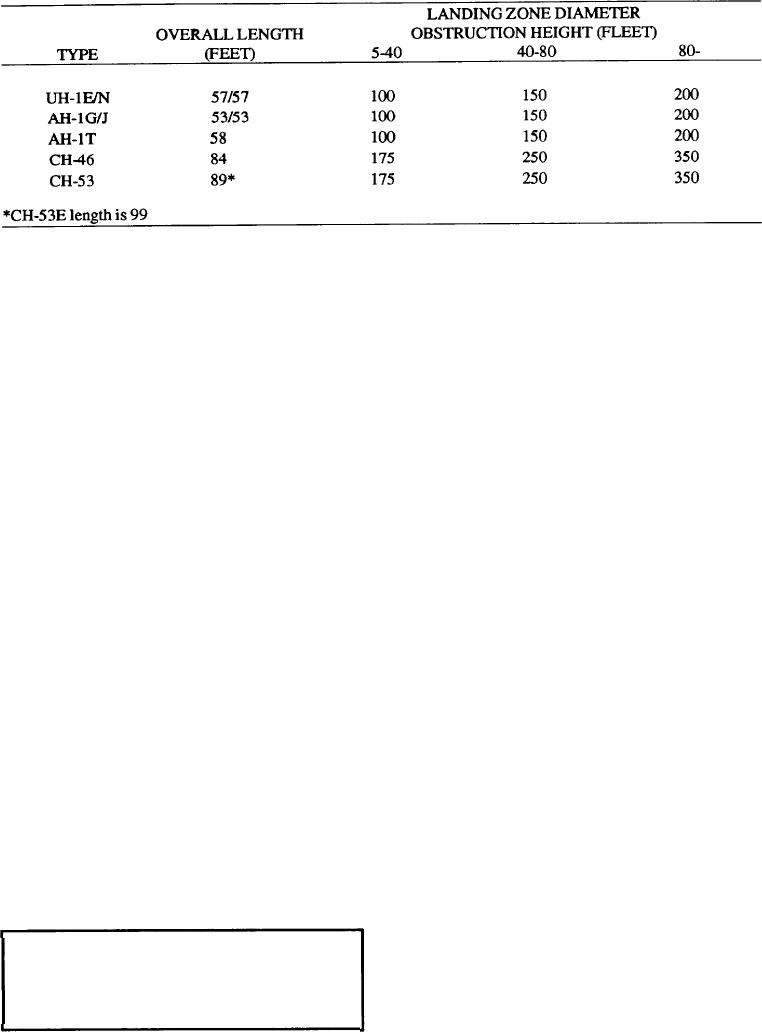
Figure 3-4.--Landing zone diameter.
2. Night landing: The organization and use of an
Recommendations for marking an LZ and for guiding
LZ at night or during periods of low visibility is more
a helicopter to an LZ are as follows:
complex compared to daytime operations. Special
1. Daylight landing: The landing zone is
lighting equipment or field expedients as required.
equipped with a means of showing wind direction and
a. You must indicate outlines of landing zones
velocity. This is usually accomplished by the use of
by low-intensity markers.
smoke or by verbal radio message. Expedient methods
for determining wind direction and velocity are as
b. You must show obstacles near the landing
follows:
zone by low-intensity markers or voice radio
instructions.
a. Grass drop method. Extend your arm
straight out and drop the grass from your hand. Point
Another method of guiding the aircraft to the zone
the extended arm at the dropped grass on the ground.
is vector instructions. This is simply relaying
The angle between the arm and the body divided by four
instructions to the pilot by radio. For example, the
is the wind velocity in knots.
radio operator spots the helicopter. Using a compass,
b. Angle of smoke method. Observe the
the radio operator shoots an azimuth of 135 degrees
angle at which smoke blows. The wind speed is as
from the LZ to the helicopter and quickly computes a
follows:
back azimuth of 315 degrees. The radio operator then
transmits the following message:
--If smoke goes straight up, no wind.
"HOME WISH, THIS IS FLIGHT BEE . . .
--If smoke blows at a 30-degree angle, wind
VECTOR THREE ONE FIVE TO LANDING ZONE
is 3-5 knots.
HAWK . . . OVER."
--If smoke blows at a 60-degree angle,
The pilot then acknowledges the message and takes up
wind is 5-7 knots.
the correct heading of 315 degrees. The term vector is
--If smoke blows along the ground, wind
always used in a situation like this to prevent
exceeds 8 knots.
misunderstanding. As the helicopter approaches, minor
corrections will probably be necessary. These are given
Use smoke and landing zone panels to mark a
landing zone by day. Both should be the same color
as corrections to the original heading b y the following:
as the designation of the landing zone. This will aid
"HOME WISH, THIS IS FLIGHT BEE. . . COME
the pilot in locating the landing zone, Mark obstacles
RIGHT FIVE DEGREES OF PRESENT COURSE. . .
that cannot be removed within the landing zone with
OVER."
single red panels staked to prevent uprooting by rotor
wash.
When the tactical situation does not allow the use
of a compass, you can vector the helicopter to an LZ
SECURITY CAUTION: If smoke is used to mark the
by using the clock system:
landing zone, use only as needed and do not tell the
"HOME WISH, THIS IS FLIGHT BEE . . . MY
pilot the color of smoke; ask the pilot to acknowledge
POSITION IS AT YOUR NINE O'CLOCK . . .
the color after the smoke grenade is set off.
OVER."
3-3

