Table 15-2.-Methods of Underground Exploration and Sampling
Common name
of method
Auger boring
Well drilling
Rotary drilling
Test pits
Materials in
which used
Cohesive soils
and cohesion-
less soils above
groundwater
elevation
All soils, rock,
and boulders
All soils, rock,
and boulders
All soils. Lower-
ing of ground-
water may be
necessary
Method of
advancing the hole
Augers rotated until
filled with soil and
then removed to
surface
Churn drilling with
power machine
Rotating bits operat-
ing in a heavy
circulating liquid
Hand digging or
power excavation
Method of
Value for
sampling
foundation purposes
Samples recovered
from material
brought up on
augers
Bailed sample of
churned material
or clay socket
Samples recovered
from circulating
liquid
Samples taken by
hand from orig-
inal position in
ground
Satisfactory for high-
way exploration at
shallow depths
Clay socket samples
are dry samples
Bailed samples are
valueless
Samples are of no
value
Materials can be in-
spected in natural
condition and
place
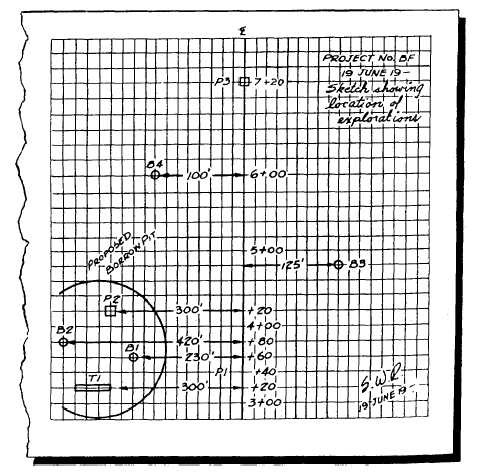
Figure 15-3.-Sketch showing locations of soil exploration points.
15-8