CHAPTER 18
SOIL STABILIZATION
Soil stabilization may be broadly defined as the
alteration or preservation of one or more soil properties
to improve the engineering characteristics and
performance of a soil. This chapter is intended to
provide you with a brief overview of soil stabilization
in terms of (1) stabilization methods, (2) the types and
selection of various chemical stabilizers used in soil
stabilization and (3) general guidance and information
relative to the design and testing of soil-cement and
soil-bituminous mixtures. For a thorough understanding
of the subject of soil stabilization, you should combine
the study of this chapter with the study of the various
references cited within the chapter.
METHODS OF STABILIZATION
The two general methods of stabilization are
mechanical and additive. The effectiveness of
stabilization depends upon the ability to obtain
uniformity in blending the various materials. Mixing in
a stationary or traveling plant is preferred; however,
other means of mixing, such as scarifies, plows, disks,
graders, and rotary mixers, have been satisfactory.
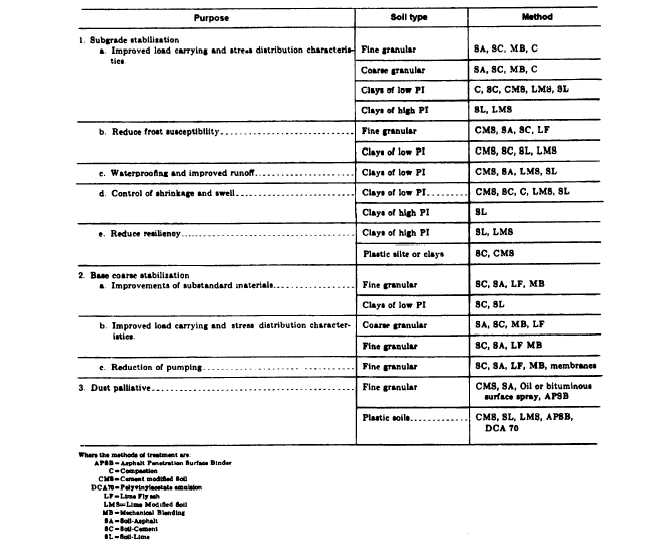
The method of soil stabilization is determined by
the amount of stabilizing required and the conditions
encountered on the project. An accurate soil description
and classification is essential to the selection of the
correct materials and procedures. Table 18-1 lists the
Table 18-1.—Stabilization Methods Most Suitable for Specific Applications
18-1