TYPES OF MATERIAL
To satisfy the requirements of material reporting
and accounting, the Navy divides material into five
categories: (1) equipment, (2) equipage, (3) repair parts,
(4) consumable supplies, and (5) services. We’ll explain
each one in the next paragraphs.
Equipment is any fictional electronic, ordnance,
hull, mechanical, or electrical unit that is operated singly
or as a component of a system or subsystem and that is
identified by a Component Identification Descrip-
tion/Allowance Parts List (CID/APL). Examples of
equipment are turbines, pumps, and electric motors.
Equipage is an item of a durable nature that is not
altered or consumed in use. The allowance of equipage
usually is determined on an individual ship basis and is
contained in the Allowance Parts Lists (APLs),
Allowance Equipage Lists (AELs), or other authoriza-
tion issued by commands, bureaus, or offices. Equipage
items differ from equipment in that they are usually
portable. Certain items of equipage are designated
“controlled equipage” and require increased manage-
ment control for the following reasons:
l
l
l
l
High unit cost
Vulnerability to pilferage
Essentiality to the ship’s mission
Personnel safety
NAVSUPPub 485, appendix II, lists items designated
as controlled equipage. Those items requiring custodial
signatures are identified by asterisks.
A repair part is any item that appears in an APL, a
manufacturer’s instruction book, technical manual, or a
similar parts list. Consumable materials such as gaskets,
which have an equipment application, are also
considered repair parts.
Consumable supplies are administrative and
housekeeping items, general-purpose hardware,
common tools, or any other item not specifically defined
as equipage or repair parts.
Services are nonmaterial requirements such as equipment
rental, commercial telephone, pilotage, and tug hire.
IDENTIFICATION OF MATERIAL
Rarely do any two persons see the same details of
the same object, much less describe them in the same
words. This need for a brief, accurate means to identify
one specific item of material led to the Federal Catalog
System presently in use throughout the DOD and civil
agencies of the government. This system requires that
only one identification number be assigned to a specific
item of material used by and carried under centralized
inventory control of any civil or military agency of the
Federal Government. The Federal Catalog System
includes the requirement to name, describe, classify, and
number all items, and to publish catalogs and stock and
identification lists.
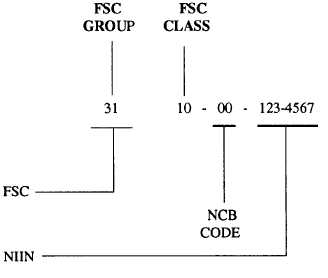
NATIONAL STOCK NUMBERS
The national stock number (NSN) consists of 13
digits and is the common language of material
identification. The first four digits of the NSN make up
the Federal Supply Classification (FSC), which has two
elements: group and class.
The FSC consists of 76 groups, some of which are
shown in the following list. NAVSUP P-485 contains a
complete list of assigned groups.
GROUP
TITLE
31
Bearings
43
Pumps and Compressors
48
Valves
59
Electrical and Electronic System
Components
79
Cleaning Supplies
The remaining nine digits of the NSN make up the
national item identification number (NIIN). The NIIN
consists of a two-digit NCB (National Codification
Bureau) code and seven digits, which, in conjunction
with the NCB code, uniquely identifies each NSN item
in the Federal supply distribution system. For example:
5-3