immobilized the injured part. This may prove to be
lifesaving in cases of severe bone fractures or spinal
cord injuries, because a jagged bone may sever nerves
and blood vessels, damage tissues, and increase shock.
Of course, the threat of fire and other similar situations
may require that the victim be moved. But the principle
should always be kept firmly in mind and considered
against other factors.
7. When transporting an injured person, always
make sure the litter is carried feet forward no matter
what injuries the victim has. This enables the rear bearer
to observe the victim for any respiratory obstruction or
breathing problem.
8. Keep the injured person comfortably warm-
warm enough to maintain normal body temperature.
Very serious and mutilating injuries may require
Figure 10-1.--Universal distress signal.
heroic first-aid measures on your part. Most injuries
require minimum physical effort but a maximum effort
in judgment and self-control to prevent everyone from
efforts to remove the obstruction. Observe the victim
trying to do too much.
closely for increased distress, and be prepared to treat
Basic life support is a term you have probably
him for a completely blocked airway.
heard before. It consists of emergency techniques
When there is inadequate air exchange, which is
for recognizing and treating failures of the
indicated by a weak or ineffective cough, high-pitched
respiratory system and heart function. The primary
noises while the victim attempts to inhale, and bluish
emphasis is placed on maintaining an open
discoloration of the skin (especially around the nails and
AIRWAY to counter upper-airway obstruction,
lips), handle the problem as though it were a complete
restoring BREATHING to counter respiratory
airway obstruction.
arrest, and restoring CIRCULATION to counter
COMPLETE AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION.
cardiac arrest. These are the ABCs of basic life
Complete airway obstruction is indicated by no air
support. This chapter attempts to cover some of the
exchange and an inability to speak, cough, or breathe. If
essentials of basic life support. Remember: this
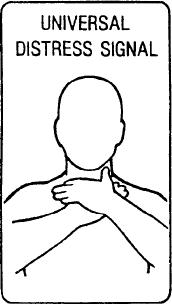
the victim is conscious, he may exhibit the universal
chapter does not substitute for a formal course in
distress signal, as identified above.
basic life support. Formal courses, such as those
given by the American Red Cross or the American
When the victim is unconscious, check for
Heart Association, provide hands-on training,
breathing. When the victim is not breathing, his
using manikins. This training is essential for proper
tongue or some other object may be blocking the
execution of the emergency techniques necessary
air passage. The airway may be opened by tilting
in basic life support.
his head back and lifting his chin. Or when his head
should not be moved, in the case of neck injuries,
his jaw may be thrust forward. These techniques
UPPER AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION
are described below.
Most people who are choking automatically clutch
OPEN THE AIRWAY
at their throat. This is recognized as the universal
distress signal for upper airway obstruction (fig. 10-1).
The most common cause of upper airway obstruction in
The most important action for successful
a conscious person is improperly chewed food.
resuscitation is to open the airway immediately. In the
PARTIAL OBSTRUCTION. When the victim
absence of sufficient muscle tone, the tongue or
coughs or when there is adequate air exchange,
epiglottis will obstruct the pharynx or the larynx,
respectively (fig. 10-2, Top). The tongue is the most
encourage the victim to continue with his own efforts to
common cause of obstruction in an unconscious victim.
expel the foreign body. Do not interfere with the victim's
10-2

