roofing materials that require continuous support
should be laid closed (without spacing); however,
when wood shingles or shakes are used in
damp climates, it is common to have spaced roof
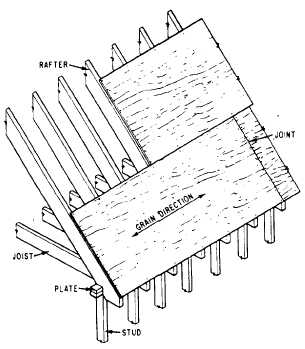
boards (fig. 6-39). When plywood roof sheathing
is used, it should be laid with the grain
perpendicular to the rafter (fig. 6-40).
Roof covering materials used for pitched roofs
are wood, asphalt shingles, tiles and slate,
galvanized iron (GI) sheets, and several other sheet
materials. For flat or low-pitched roofs, a
built-up construction is also used. An asphalt-
saturated felt underpayment called ROOFING
FELT is applied over the roof sheathing before
the roof covering is installed. The roofing felt
serves three basic purposes: It keeps the roof
sheathing dry until the shingles can be applied,
it acts as a secondary barrier against wind-driven
rain and snow, and it protects the shingles from
any resinous substance that may be released from
the sheathing.
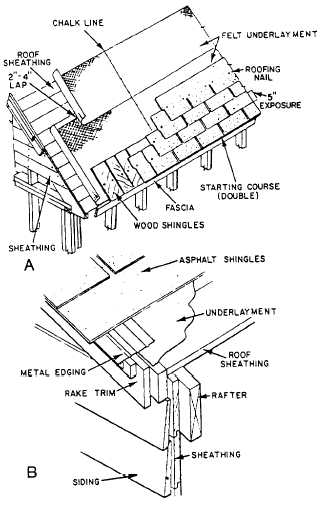
The method of laying an asphalt-shingle roof
is shown in figure 6-41. The roofing rolls are
usually 36 in. wide with a 2 in. to 4 in. overlap.
The shingles are usually laid with 5 in. exposed
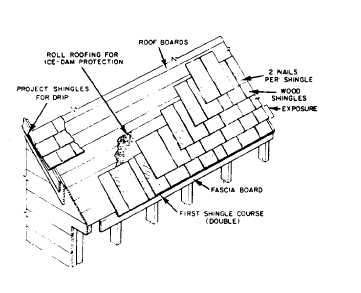
to the weather. Figure 6-42 shows installation of
wood shingles. Wood shingles are available in
Figure 6-40.-Application of plywood roof sheathing.
Figure 6-41.-Application of asphalt shingles: A. Common
method with strip shingles; B. Metal edging at gable
end.
Figure 6-42.-Installation of wood shingles.
6-28