development of symptoms is often confusing
when an attempt is made to determine the time
or location where the contact with the plant
occurred. The itching sensation and subsequent
inflammation that usually develops into watery
blisters under the skin may continue for several
days from a single contamination. Persistence of
symptoms over a long period is most likely caused
by new contacts with plants or by contact with
previously contaminated clothing or animals.
Severe infection may produce more serious
symptoms that result in much pain through
abscesses,
enlarged glands, fever, or other
complications. Secondary infections are always
a possibility in any break in the skin that occurs
when the watery blisters break.
With poison ivy, the next development is
usually the appearance of a scabrous, deep red
rash over large skin areas. With poison, sumac,
it is usually the appearance of large blisters, filled
with a thick yellowish white liquid strongly
resembling pus. When the blisters break, this
liquid runs over adjacent skin areas and, thus,
enlarges the area of infection.
The resinous juice exuded by these poisonous
plants is almost entirely nonvolatile; that is,
nonevaporating or will not dry up. Consequently,
the juice may be carried on clothing, shoes, tools,
or soil for long periods. In this way, it may infect
persons who have actually not come into contact
with the plants themselves. Individuals have, in
fact, been severely infected by juice carried
through air by smoke from burning plants. Other
persons have been infected by resinous juice being
carried on the fur of animals.
Figure 12-29.-Poison oak (leaves and fruit).
To avoid contact with the plants themselves,
you must have an idea of what they look like.
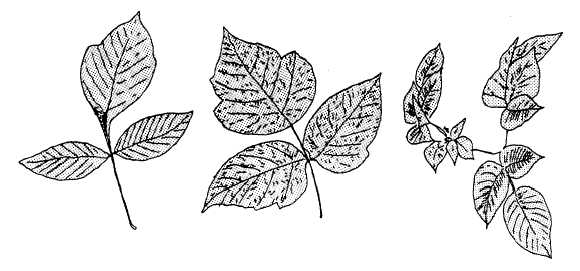
Poison ivy has a trefoil (three leaflet) leaf, as
shown in figure 12-28. The upper surface of the
leaflet has a shiny, varnished appearance. The
variety called poison oak has a leaflet with a
serrated, or lobed, edge like that of an oak leaf,
as shown in figure 12-29. Ordinary poison ivy is
Figure 12-28.-Different varieties
12-29
of poison ivy leaves.