G
L
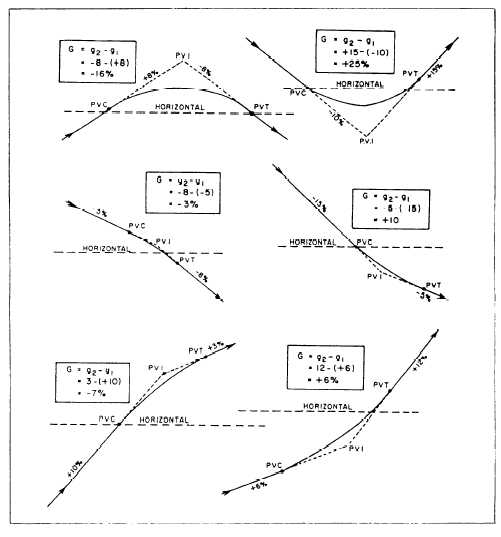
The algebraic difference of the grades:
G = g2 -g,,
wherein plus values are assigned to uphill
grades and minus values to downhill grades;
examples of various algebraic differences are
shown later in this section.
Length of the curve; the horizontal length
measured in 100-foot stations from the PVC to
the PVT. This length may be computed using
the formula L = G/r, where r is the rate of
change (usually given in the design criteria).
When the rate of change is not given, L (in
stations) can be computed as follows: for a
summit curve, L = 125 x G/4; for a sag curve,
L = 100 x G/4. If L does not come out to a whole
number of stations using these formulas, then
it is usually extended to the nearest whole
number. You should note that these formulas
for length are for road design only, NOT
railway.
1]
Horizontal length of the portion of the PVC
to the PVI; measured in feet.
12
Horizontal length of the portion of the curve
form the PVI to the PVT; measured in feet.
e
Vertical (external) distance from the PVI to the
curve, measured in feet. This distance is
computed using the formula e = LG/8, where
L is the total length in stations and G is the
algebraic difference of the grades in percent.
Figure 11-16.—Algebraic differences of grades.
11-14