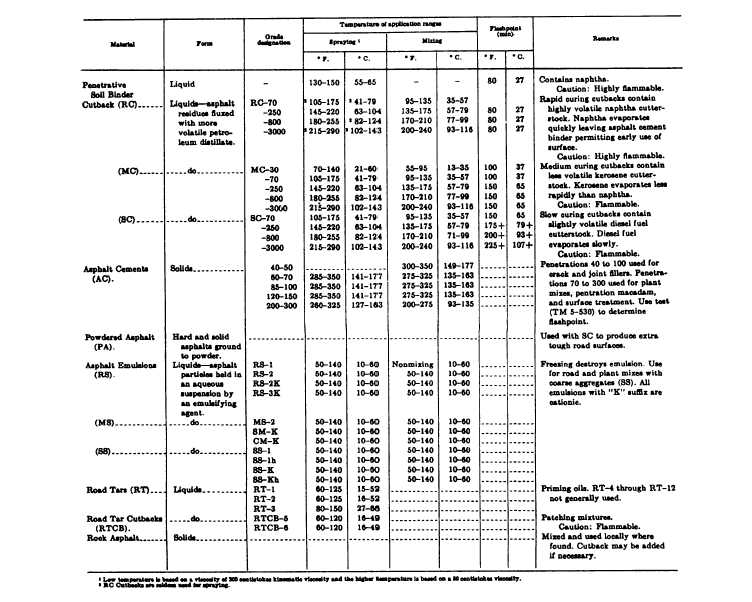
Table 13-6.-Characteristics of Bituminous Materials
cutback asphalt, but differs in many specific properties.
It is used as a soil binder and dust palliative.
EMULSIONS.– Emulsification is the third process
in which asphalt is liquified. In the emulsification
process, hot asphalt cement is mechanically separated
into minute globules and is dispersed in water that is
treated with a small quantity of an emulsifying agent,
such as soap, colloidal clay, or one of numerous other
organic agents. The rate at which the asphalt globules
separate from the water is called the breaking or setting
time. This rate is generally dependent upon the
emulsifier used and the proportion of water to asphalt.
Based in the breaking time, emulsions are described
as rapid setting (RS), medium setting (MS), and slow
setting (SS). They are also described by viscosity
numbers (fig. 13-28).
Emulsions are also grouped according to their
ability to mix with damp aggregate. The RS emulsion
breaks so fast that it cannot be mixed; therefore, it is
called a nonmixing emulsion. The MS and SS emulsions
break slowly enough to permit good mixing; that is, each
particle of the aggregate is uniformly coated. Emulsions
may be satisfactorily used as a tack coat for bituminous
pavements.
ROAD TARS.— Tars are products of the
distillation of coal. No natural sources of tar exist. Coal
tar is a general term applied to all varieties of tar
obtained from coal. It is produced by one of several
methods, depending on the desired end product. When
.
13-38
----------
L– .