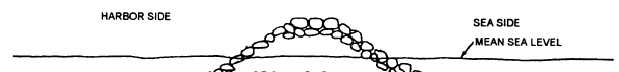
Figure 1-13.—Rubble-mound breakwater or jetty.
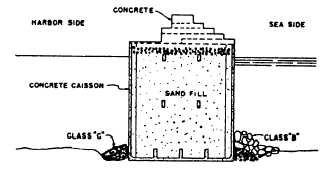
Figure 1-14.—Composite breakwater or jetty.
WATERFRONT STRUCTURES
Waterfront structures may be broadly divided into
three types as fpllows: (1) harbor-shelter structures,
(2) stable-shoreline structures, and (3) wharfage
structures.
HARBOR-SHELTER STRUCTURES
Harbor-shelter structures are offshore structures
that are designed to create a sheltered harbor. Various
types of these structures are discussed below.
A breakwater is an offshore barrier, erected to
break the action of the waves and thereby maintain an
area of calm water inside the breakwater. A jetty is a
similar structure, except that its main purpose is to direct
the current or tidal flow along the line of a selected
channel.
The simplest type of breakwater or jetty is the
rubble-mound (also called rock-mound) type shown in
figure 1-13. The width of its cap may vary from 15 to
Figure 1-15.—Caisson breakwater or jetty.
70 feet. The width of its base depends on the width of
the cap, height of the structure, and the slopes of the
inner and outer faces. For a deepwater site or from
with an extra-high tide range, a rubble-mound
breakwater may be topped with a concrete cap structure,
such as shown in figure 1-14. A structure of this type is
called a composite breakwater or jetty. In figure 1-14,
the cap structure is made of a series of precast concrete
1-8