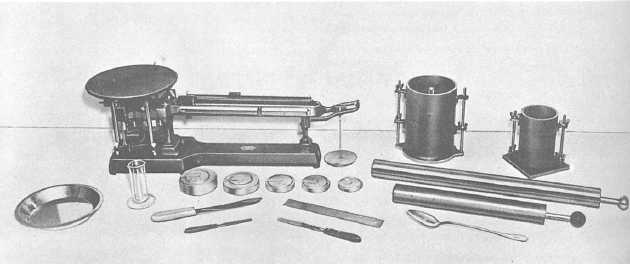
Figure 13-1.—Apparatus for soil compaction testing.
fitted with a detachable base plate and a removable
extension collar that is 2 1/2 inches high.
The larger cylinder is the CBR mold. It is 6
inches in diameter, 7 inches high, and is fitted with a
base plate and a 2-inch-high extension collar. When
you are compacting a soil sample, a 2 1/2-inch-thick
spacer disk is placed inside the CBR mold to control
the thickness of the compacted sample. With the
spacer disk in place, the volume of the mold is about
0.0735 cubic feet. The CBR mold is used for samples
containing material retained on the No. 4 sieve.
The compaction tamper consists of a drop tamper
in a cylindrical guide. The tamper has a drop weight
that weighs 10 pounds and has a striking face that is
2 inches in diameter. The guide sleeve regulates the
height of drop to 18 inches. To use the compaction
tamper, you place the guide on top of the specimen
and then draw the tamper to the top of the guide and
allow it to drop.
Other items that you need to perform compaction
testing are a balance or scale for weighing the
material in grams, a 3/4-inch and a No. 4 sieve,
moisture canisters, and tools, such as a mixing pan,
spoon, trowel, spatula, and a steel straightedge for
striking excess material from the top of the mold after
compaction.
Sample Preparation and Compaction
Procedures
About five specimens, containing successively
increasing moisture contents, are needed to
determine the OMC at which the maximum density
for a given compactive effort will occur. For the
Proctor mold, about 6 pounds for each specimen
(about 30 pounds total) is needed. For the CBR mold,
you will need about 12 to 14 pounds per specimen, or
about 60 to 70 pounds total.
Before the compacting begins, the sample is air-
dried and a moisture content of the air-dried material
is determined. Airdrying is done by spreading out the
material in the sun or in front of an electric fan. The
water content of the air-dried material is determined
as a basis for estimating the amount of water you
need to add to each trial specimen. The driest
specimen should contain just enough water to
produce a damp mixture that crumbles readily. For
each succeeding specimen, increase the water content
by about 2 percent until the wettest specimen is quite
wet and plastic.
The compaction procedures for nongravelly and
gravelly soils are the same with two exceptions. First,
the 4-inch Proctor mold is used for fine-grained soil,
and the CBR mold is used for gravelly soil. Second, 25
tamper blows per layer are used for the Proctor mold,
and 55 blows per layer are used in the CBR mold.
That results in equal compactive efforts for the two
mold sizes and soil volumes.
To compact the soil, you first attach the base
plate and collar to the mold. Then you fill the mold to
the top of the collar with the material placed in five
equal layers, compacting each layer with the
appropriate 25 or 55 equally distributed blows. After
compacting the
13-2