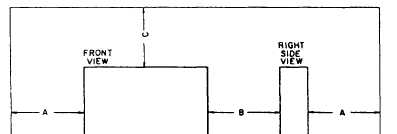
Figure 5-15.-Improved spacing for three-view projection of object shown in figure 5-18.
figure 5-14, you can now call the front; it follows
that which appears as the front in figure 5-14
appears as the bottom in figure 5-15. Again the
right side view appears, but it now appears in the
upper, rather than the lower, right corner and
vertically rather than horizontally.
Spacing views in a drawing of a circular
object is like spacing letters; you try to equalize
the areas of the spaces around and between the
views. Figure 5-16 shows properly spaced two-
view drawings of a perforated disk. For the
views that are horizontally in line, you locate
the horizontal center line midway between the
horizontal margins; for the views that are
vertically in line, you locate it midway between
the vertical margins. The other spacing is as
indicated. To determine the lengths of distances
A and 2/3 A, set a compass to the diameter plus
the thickness of the disk, and lay off this distance
on the margin. Then divide the remaining segment
of the margin into three intervals, two of them
being equal, and the third one being 1 1/2 times
as long as each of the others.
VIEW ANALYSIS.— You must be able to
analyze a multi-view projection or, in other words,
to determine what each line in a particular view
represents. In this connection, it is helpful to
remember that in a third-angle projection, the
plane of projection is always presumed to be
between the object and the observer, regardless
Figure 5-16.-Spacing of views of a circular object,
5-9