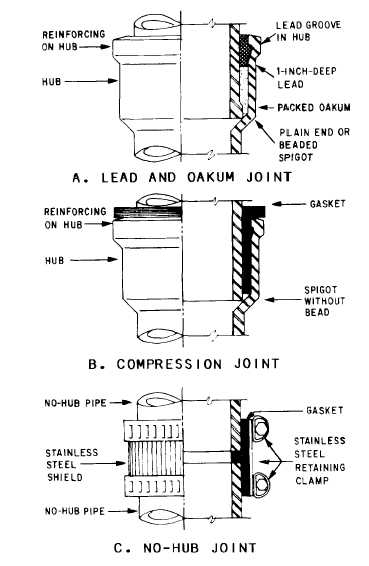
Figure 8-17.-Various joints currently used to connect CISP
and fittings.
Joints and Connections
Various types of joints and connections
used in waste drainage systems are described
below.
LEAD AND OAKUM JOINT, COMPRES-
SION JOINT, AND NO-HUB JOINT.— These
types of joints (fig. 8-17) are used to connect
cast-iron soil pipes (CISP) and fittings. In lead
and oakum joints, oakum (made of hemp im-
pregnated with bituminous compound and loosely
twisted or spun into a rope or yarn) is packed
into the hub completely around the joint, and
melted lead is poured over it (fig. 8-17, view A).
In compression joints, an assembly tool is used
to force the spigot end of the pipe or fitting into
the lubricated gasket inside the hub (fig. 8-17, view
B). A no-hub joint uses a gasket on the end of
one pipe and a stainless steel shield and clamp
assembly on the end of the other pipe (fig. 8-17,
view C).
MORTAR OR BITUMINOUS JOINTS.—
This type of joint is common to vitrified clay and
concrete pipes and fittings. Mortar joints may be
made of grout (a mixture of cement, sand, and
water).
The use of SPEED SEAL JOINTS (rubber
rings) in joining vitrified clay pipe has become
widespread. Speed seal joints eliminate the use of
oakum and mortar joints for sewer mains. This
type of seal is made a part of the vitrified pipe
joint when manufactured. It is made of polyvinyl
chloride and is called a plastisol joint connection.
Traps
A trap is a device that catches and holds a
quantity of water, thus forming a seal that
prevents the gases resulting from sewage decom-
position from entering the building through the
pipe. A number of different types of traps are
available; however, the trap mainly used with
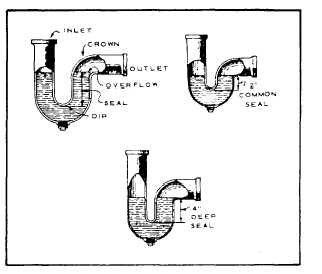
plumbing fixtures is the P-TRAP (fig. 8-18). It
comes in sizes from 1 1/4 in. to 6 in. in diameter.
P-traps are usually made of nickel or chrome-
plated brass, malleable galvanized or wrought
iron, copper, other metal alloys, and plastic.
Figure 8-18.-P-traps.
8-14