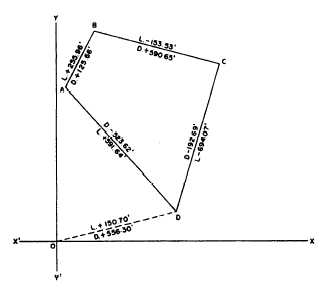
Figure 7-18.—Closed traverse with adjusted latitudes and
departures.
departures. Figure 7-18 shows a closed traverse with
adjusted latitudes and departures notes. You want to
assign plane coordinates to the traverse stations. To
avoid the necessity of working with negative
coordinates, you select as point of origin a point O that
is west of the most westerly traverse station and south
of the most southerly traverse station.
You determine the bearing and length of dotted line
OD and compute from these values the latitude and
departure of OD. You can see that the Y coordinate of
station D must equal the latitude of OD, or 150.70 feet
Also the X coordinate of D must equal the departure of
OD or 556.30 feet.
The Y coordinate of station A equals the Y
coordinate of D plus the latitude of AD or
150.70 + 591.64 = 742.34 ft.
The X coordinate of station A equals the X
coordinate of D minus the departure of AD or
556.30 – 523.62 = 32.68 ft.
The Y coordinate of station B equals the Y
coordinate of station A plus the latitude of AB or
742.34 + 255.96 = 998.30 ft.
The X coordinate of station B equals the X
coordinate of station A plus the departure of AB or
32.68 + 125.66 = 158.34 ft.
The Y coordinate of station C equals the Y
coordinate of station B minus the latitude of C or
998.30 – 153.53 = 844.77 ft.
The X coordinate of station C equals the X
coordinate of station B plus the departure of BC or
158.34 + 590.65 = 748.99 ft.
The Y coordinate of station D equals the Y
coordinate of station C minus the latitude of CD or
844.77 – 694.07 = 150.70 ft.
The X coordinate of station D equals the X
coordinate of station C minus the departure of CD or
748.99 – 192.69 = 556.30 ft.
These are the same coordinates you originally
computed for station D, a fact that serves as a check on
your accuracy.
You enter these values on a form that is similar to
the one shown in figure 7-19. In actual practice,
however, you will use a wider form on which all values
and computations from the original station through
bearing and distance, latitude and departure, and
coordinates can be entered.
LATITUDE AND DEPARTURE FROM PLANE
COORDINATES.— The numerical values of latitude
and departure of a traverse line are easily computed
from the coordinates of the end stations of the line. For
traverse line AB, for example, the numerical value of
latitude equals the difference between the Y coordinate
of A and the Y coordinate of B, while the numerical value
of departure equals the difference between the X
coordinate of A and the X coordinate of B.
To determine whether a latitude or departure
computed this way is positive or negative, the best
method is to examine a sketch of the traverse to
determine the compass direction of the bearing of the
line in question. If the line bears northeast, the latitude
is positive, or north, and the departure is positive, or east.
If the line bears southwest, both latitude and departure
are negative.
Computing Areas
Various methods are used in computing areas. Some
of the common methods with which the EA should be
familiar are discussed below.
7-14