3.
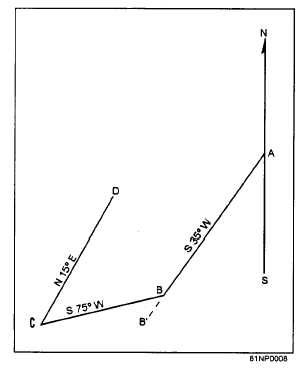
Figure 10D
IN ANSWERING QUESTIONS 10-8 THROUGH 10-10,
REFER TO FIGURE 10D.
10-8.
What is the size of the deflection
angle between traverse lines BC
and CD?
1.
60°
2.
90°
3.
105°
4.
120°
10-9.
How many degrees are there in the
exterior angle ABC?
1.
205°
2.
215°
3.
220°
4.
235°
10-10.
How many degrees are there in the
interior angle ABC?
1.
120°
2.
130°
3.
140°
4.
150°
10-11.
TO convert a bearing in the
quadrant to the equivalent
azimuth, you must use which
following calculations?
1.
Add 90° to the bearinq
SE
of the
1.
2.
Add 180°
3.
Subtract
4.
Subtract
to the bearing
the bearing from 180°
the bearing from 360°
10-12.
Assume that a measured forward
bearing on a compass-tape survey
was N15°35’W and the back bearing
on the same line was S15°15’E.
The difference was probably caused
by which of the following
conditions ?
1.
Declination
2.
Local attraction
3.
An error in reading the
compass
4.
A defect in the compass
mechanism
10-13.
The magnetic declination at a
given point on the surface of the
earth is the horizontal angle that
the magnetic meridian makes with
what line?
1.
The agonic line
2.
The true meridian
The isogonic line
4.
The assumed meridian
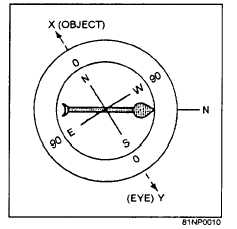
Figure 10E
IN ANSWERING QUESTIONS 10-14 THROUGH
10-16, REFER TO FIGURE 10E.
10-14.
What is the approximate compass
bearing of the object?
1.
Due north
2.
S70°W
3.
S30°W
4.
S30°E
10-15.
What is the approximate magnetic
bearing of the object if the local
attraction is 20°E?
Due west
2.
S50°W
3.
Due south
4.
N20°W
67