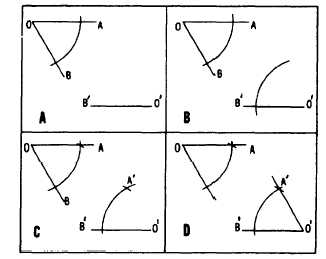
Figure 4-10.-Transferring an angle.
equal in size to one that is already drawn.
This procedure, called transferring an- angle, is
shown in figure 4-10. Here, the draftsman desired
to lay off from O´ a line that would make an angle
with B´O´ equal to angle BOA. To do this, draw
an arc through OB and OA, with O as a center,
as shown in figure 4-10, view A. Then, draw an
arc of the same radius from B´O´, with O´ as a
center, as shown in figure 4-10, view B. Next,
measure the length of the chord of the arc
between OB and OA and lay off the same length
on the arc from B´O´, as shown in figure 4-10,
view C. A line drawn from O´ through A´ makes
an angle with B´O´ equal to angle BOA, as shown
in figure 4-10, view D.
BISECTION OF AN ANGLE
To bisect an angle means to divide it in half.
If you know the size of the angle, you can bisect
it by simply dividing the size by 2 and laying off
the result with a protractor.
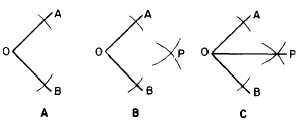
Geometric construction for bisecting an angle
is shown in figure 4-11, To bisect the angle AOB,
first lay off equal intervals from O on OA and
OB. With the ends of these intervals as centers,
strike intersecting arcs of equal radius at P. Draw
a line from O through the point of intersection
of the arcs, P. The line OP bisects angle AOB.
PLANE FIGURES
This section explains how to construct certain
plane figures, such as the triangle, rectangle,
square, and regular polygon. You must under-
stand the geometrical construction of plane figures
because they appear in engineering drawings.
Figure 4-11.-Bisecting an angle.
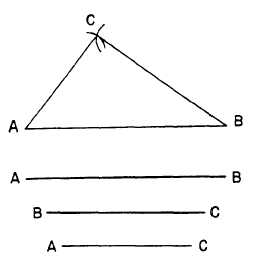
Figure 4-12.-Constructing a triangle with three sides given.
TRIANGLE: THREE SIDES GIVEN
To draw a triangle with three sides given, first
draw a straight line AB, equal in length to one
of the given sides (fig. 4-12). With A as a center,
strike an arc with a radius equal to the given length
of the second side. With B as a center, strike an
intersecting arc with a radius equal to the length
of the third side. Draw lines from A and B to the
point of intersection of the arcs.
RIGHT TRIANGLE: HYPOTENUSE
AND ONE SIDE GIVEN
Figure 4-13 shows a method of drawing a right
triangle when the hypotenuse and one side are
given. The line H is the given hypotenuse; the line
S is the given side. Draw AB equal to H. Locate
the center of AB (by bisection), and, with the
midpoint as a center and a radius equal to one-
half of AB, draw the semicircle from A to B as
shown. Set a compass or dividers to the length
of S, and, with A as a center, strike an arc
intersecting the semicircle at C. Draw AC
and BC.
4-4