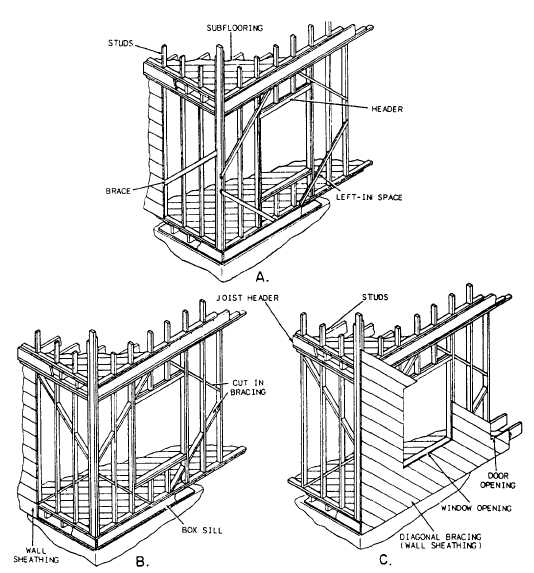
Figure 6-22.-Common types of bracing: A. Let-in bracing; B. Cut-in bracing; C. Diagonal bracing.
Braces
Braces are used to stiffen framed construction
and help buildings resist the twisting or straining
effects of wind or storm. Good bracing keeps
corners square and plumb and prevents warping,
sagging, and shifts resulting from lateral and
external forces that would otherwise tend to
distort the frame. Figure 6-22 shows three
common methods of bracing frame structures:
(A) let-in bracing, (B) cut-in bracing, and
(C) diagonal bracing.
ROOF FRAMING
Roofs must be sloped so that they will
shed water. The most common types of roof
construction include the intersecting, the shed, the
gable, and the hip (fig. 6-23). An INTER-
SECTING ROOF consists of a gable and valley
or hip and valley intersecting each other at right
angles. A SHED ROOF has a single surface that
slopes downward from a ridge on one side of the
structure. A GABLE ROOF has two surfaces
sloping downward from a ridge located between
the sides of the structure—usually midway
between them. A HIP ROOF is pitched on the
sides like a gable roof and also is pitched on one
or both ends.
Roof Pitch
The PITCH (amount of slope) of a roof is
expressed as a FRACTION in which the
6-20