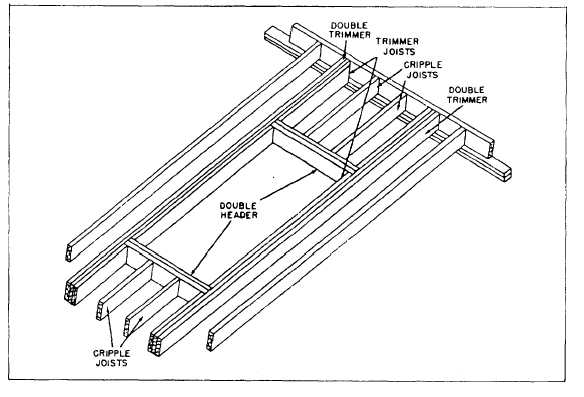
Figure 6-17.-Framing around floor openings.
Bridging
Bridging is the system of bracing the joists to
each other to hold them plumb and aligned. It
also serves to distribute part of a concentrated
load over several joists next to those directly under
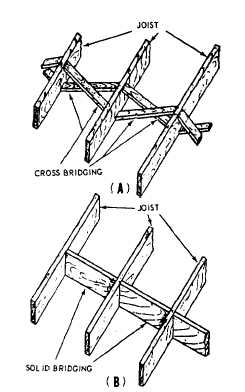
the load. There are two types of bridging: CROSS
BRIDGING (fig. 6-18, view A) and SOLID
BRIDGING (fig, 6-18, view B). Cross bridging
consists of pairs of STRUTS set diagonally
between the joists. The strut stock comes in sizes
of 1 by 3, 1 by 4, 2 by 2, and 2 by 4. Solid
bridging consists of pieces of joist-size stock set
at right angles to the joists. They can be staggered
for easier installation. Cross bridging is more rigid
than solid bridging and is more frequently used
in construction. Bridging should be provided for
all spans greater than 6 ft.
Subflooring
Joists are covered by a layer (or double layer)
of boards called SUBFLOORING. It usually
consists of square-edge or tongue-and-grooved
Figure 6-18.-Cross bridging and solid bridging.
boards or plywood 1/2 to 3/4 in. thick that serve
6-17