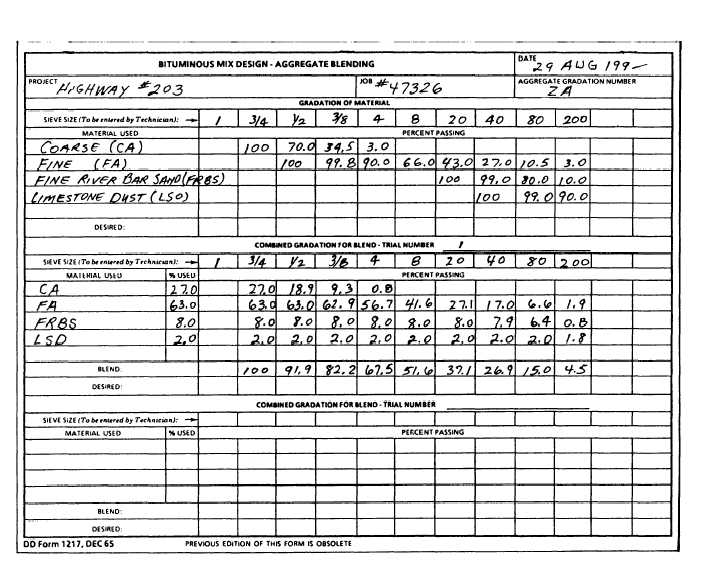
Figure 13-36.-Data sheet for aggregate gradation of trial blends (DD Form 1217).
primary roads. Seventy-five blows produce the
equivalent of a tire pressure of 200 psi; 50 blows
produce the equivalent of a tire pressure of 100 psi. After
the compaction process, place the mold in a
bearing-ratio jack and extract the compacted sample
with extraction equipment.
Density and Voids Determination
Density of the specimens should be determined by
weighing in air and in water. A direct weight in water of
open-textured or porous specimens will give erroneous
results because of absorption of water, and other means
must be used to determine the volume of the specimen.
One means of measuring the volume of a porous
specimen is to coat the specimen with paraffin to seal
.
all the voids and then weigh the coated specimen in air
and in water. A correction is made for the weight and
volume of the paraffin. The difference between these
two weights, in grams, gives the volume of the specimen
in cubic centimeters. You can then determine the unit
weight (density) of the mix in pounds per cubic foot for
each specimen by multiplying the specific gravity of the
specimen by 62.4 pounds (weight of 1 cubic foot of
water). Before carrying out the calculations for percent
of voids, you must know the specific gravity of the
aggregate blend and the asphalt content used.
Stability and Flow Determination
A full discussion of the method used to test for
stability and flow can be found in NAVFAC MO-330;
13-49